标签:
#include <exception>
Typedefs
|
exception_ptr |
一种类型,描述了一个指向异常的指针 |
|
terminate_handler |
一种类型,描述了一个适合作为terminate_handler的函数的指针 |
|
unexperted_handler |
一种类型,描述了一个适合作为unexpected_handler的函数的指针 |
Functions
|
current_exception |
获得当前异常的指针 |
|
get_terminate |
获得当前terminate_handler函数 |
|
get_unexpected |
获得当前unexpected_handler函数 |
|
make_exception_ptr |
创建一个包含exception副本的exception_ptr对象 |
|
rethrow_exception |
抛出一个以参数传递的异常 |
|
set_terminate |
建立一个新的terminate_handler,以便在程序结束时调用 |
|
set_unexpected |
建立一个新的unexpected_handler,以便在程序遇到未知类型异常时调用 |
|
terminate |
调用terminate handler |
|
uncaught_exception |
如果当前正在处理一个已经抛出的异常,那么返回ture |
|
unexpected |
调用一个未知的处理程序 |
Classes
|
bad_exception Class |
描述一种异常,该异常可能从unexpected_handler中抛出 |
|
exception Class |
所有异常类的基类 |
/* ************************************************************************************* */
/* exception_ptr */
typedef unspecified exception_ptr;
说明:
指向exception对象的智能指针类型。这是一种类似shared_ptr的类型:只要还有一个exception_ptr指向exception对象,那么该exception对象就必须保持有效。可以将exception_ptr对象的生命周期延伸到catch语句块外或者不同线程之间。
对于exception_ptr类型,不同的库拥有不同的实现方式,但是其至少需要支持如下几种操作:
可以通过以下操作获得exception_ptr对象:current_exception、make_exception_ptr、nested_exception::nested_ptr;通过rethrow_exception重新抛出异常。
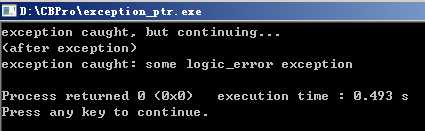
1 // exception_ptr example 2 #include <iostream> // std::cout 3 #include <exception> // std::exception_ptr, std::current_exception, std::rethrow_exception 4 #include <stdexcept> // std::logic_error 5 6 int main () 7 { 8 std::exception_ptr p; 9 try 10 { 11 throw std::logic_error("some logic_error exception"); // throws 12 } 13 catch(const std::exception& e) 14 { 15 p = std::current_exception(); 16 std::cout <<"exception caught, but continuing...\n"; 17 } 18 19 std::cout <<"(after exception)\n"; 20 21 try 22 { 23 std::rethrow_exception(p); 24 } 25 catch (const std::exception& e) 26 { 27 std::cout <<"exception caught: " << e.what() << ‘\n‘; 28 } 29 30 return 0; 31 }
/* terminate_handler */
typedef void (*terminate_handler)();
terminate_handler是一个指向void(void)函数的指针,可以用作set_terminate函数的参数和返回值。
/* unexpected_handler */
typedef void (*unexpected_handler)();
unexpected_handler是一个指向void(void)函数的指针,可以用作set_unexpected函数的参数和返回值。
/* ************************************************************************************* */
/* exception */
class exception {
public:
exception () noexcept;
exception (const exception&) noexcept;
exception& operator= (const exception&) noexcept;
virtual ~exception();
virtual const char* what() const noexcept;
}
说明:
所以标准异常类的基类,因此exception&可以适配所有的异常类型。
直接派生类:
|
bad_alloc |
allocate memory failed |
|
bad_cast |
dynamic case failed |
|
bad_exception |
unexpected handler failed |
|
bad_function_call |
bad call |
|
bad_typeid |
typeid of null pointer |
|
bad_weak_ptr |
bad weak pointer |
|
ios_base::failure |
base class for stream exceptions |
|
logic_error |
logic error |
|
runtime_error |
runtime error |
间接派生类:
|
通过logic_error派生: |
|
|
domain_error |
domain error |
|
future_error |
future error |
|
invalid_argument |
invalid argument |
|
length_error |
length error |
|
out_of_range |
out-of-range |
|
通过runtime_error派生: |
|
|
overflow_error |
overflow error |
|
range_error |
range error |
|
system_error |
system error |
|
underflow_error |
system error |
|
通过bad_alloc派生: |
|
|
bad_array_new_length |
bad array length |
|
通过system_error派生: |
|
|
ios_base::failure |
base class for stream exceptions |
示例代码:
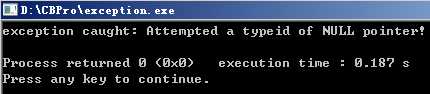
1 // exception example 2 #include <iostream> // std::cerr 3 #include <typeinfo> // operator typeid 4 #include <exception> // std::exception 5 6 class Polymorphic 7 { 8 virtual void member(){ } 9 }; 10 11 int main(){ 12 13 try 14 { 15 Polymorphic * pb = 0; 16 typeid(*pb); // throws a bad_typeid exception 17 } 18 catch(std::exception& e) 19 { 20 std::cerr << "exception caught: " << e.what() << ‘\n‘; 21 } 22 23 return 0; 24 }
/* bad_exception */
class bad_exception : public exception;
说明:
如果bad_exception在函数的throw列表中,那么unexpected将会抛出一个bad_exception来代替terminate函数或者set_unexpected指定的函数来终止程序。
1 // bad_exception example 2 #include <iostream> // std::cerr 3 #include <exception> // std::bad_exception, std::set_unexpected 4 5 void myunexpected() 6 { 7 std::cerr << "unexpected handler called\n"; 8 throw; 9 } 10 11 void myfunction() throw(char, std::string, std::bad_exception) 12 { 13 throw 100.0; // throws double (not in exception-specification) 14 } 15 16 int main(void) 17 { 18 std::set_unexpected(myunexpected); 19 try 20 { 21 myfunction(); 22 } 23 catch(int) 24 { 25 std::cerr << "caught int\n"; 26 } 27 catch(std::bad_exception be) 28 { 29 std::cerr << "caught bad_exception: "; 30 std::cerr << be.what() << "\n"; 31 } 32 catch(...) 33 { 34 std::cerr << "caught some other exception\n"; 35 } 36 37 return 0; 38 }
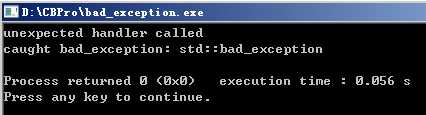
上述程序中,语句try{ myfunction(); }后并没有调用terminate()函数,也没有再次调用set_unexcepted指定的函数myunexpected(),而是调用了
catch(std::bad_exception be)
{
std::cerr << "caught bad_exception: ";
std::cerr << be.what() << "\n";
}
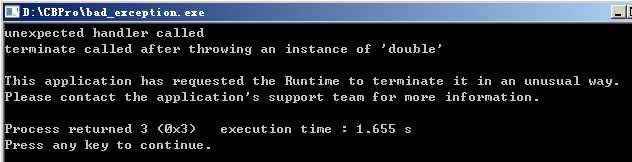
如果throw列表中没有指定std::bad_exception,那么将会调用terminate(),如下所示:
/* nested_exception */
class nested_exception {
public:
nested_exception() noexcept;
nested_exception (const nested_exception&) noexcept = default;
nested_exception& operator= (const nested_exception&) noexcept = default;
virtual ~nested_exception() = default;
[[noreturn]] void rethrow_nested() const;
exception_ptr nested_ptr() const noexcept;
}
说明:
nested exception对象通常可以通过throw_with_nested函数构造,只需要传入outer exception作为参数即可。返回的exception对象拥有与outer exception相同的属性和成员,但是其包含了与nested exception相关的额外信息以及两个用于访问nested exception的成员函数:nested_ptr和rethrow_nested。
1 // nested_exception example 2 #include <iostream> // std::cerr 3 #include <exception> // std::exception, std::throw_with_nested, std::rethrow_if_nested 4 #include <stdexcept> // std::logic_error 5 6 // recursively print exception whats: 7 void print_what(const std::exception& e) 8 { 9 std::cerr << e.what() << ‘\n‘; 10 try 11 { 12 std::rethrow_if_nested(e); 13 } 14 catch(const std::exception& nested) 15 { 16 std::cerr << "nested: "; 17 print_what(nested); 18 } 19 } 20 21 // throws an exception nested in another: 22 void throw_nested() 23 { 24 try 25 { 26 throw std::logic_error("first"); 27 } 28 catch(const std::exception& e) 29 { 30 std::throw_with_nested(std::logic_error("second")); /* outer:second; nested:first */ 31 } 32 } 33 34 int main() 35 { 36 try 37 { 38 throw_nested(); 39 } 40 catch(std::exception& e) 41 { 42 print_what(e); 43 } 44 45 return 0; 46 } 47 48 /** 49 output: 50 second 51 nested: first 52 */
exception -----> Typedefs & Classes
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/benxintuzi/p/4617073.html