标签:
1 Serial-parallel multiplier
Figure 12.1 shows the RTL diagram of a serial-parallel multiplier. One of the input vectors (a) is applied serially to the circuit (one bit at a time, starting from the LSB), while the other (b) is applied in parallel (all bits simultaneously). Say that a has M bits, while b has N. Then, after all M bits of a have been presented to the system, a string of M ‘0’s must follow, in order to complete the (M þ N)-bit output product.
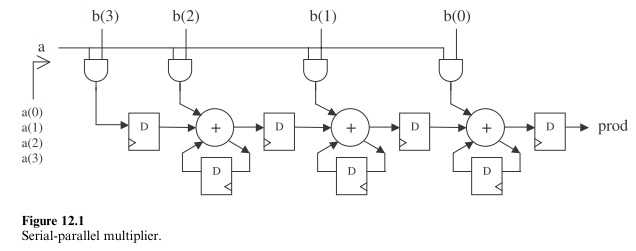
This system is pipelined, and is constructed using AND gates, full-adder units, plus registers (?ip-?ops). Each unit of the pipeline (except the leftmost one) requires one adder and two registers, plus an AND gate to compute one of the inputs. Thus for an M x N multiplier, O(N) of such units are required.
2 VHDL
1) and_2.vhd
1 library IEEE; 2 use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; 3 4 entity and_2 is 5 port 6 ( 7 a, b: in std_logic; 8 y: out std_logic 9 ); 10 end and_2; 11 12 architecture sim of and_2 is 13 begin 14 y <= a and b; 15 16 end sim;
2) reg.vhd
1 library IEEE; 2 use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; 3 4 entity reg is 5 port 6 ( 7 d, clk, rst: in std_logic; 8 q: out std_logic 9 ); 10 end reg; 11 12 architecture sim of reg is 13 begin 14 process(clk, rst) 15 begin 16 if (rst = ‘1‘) then q <= ‘0‘; 17 elsif (clk‘event and clk = ‘1‘) then q <= d; 18 end if; 19 end process; 20 21 end sim;
3) fau.vhd
1 library IEEE; 2 use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; 3 4 entity fau is 5 port 6 ( 7 a, b, cin: in std_logic; 8 s, cout: out std_logic 9 ); 10 end fau; 11 12 architecture sim of fau is 13 begin 14 s <= a xor b xor cin; 15 cout <= (a and b) or (a and cin) or (b and cin); 16 17 end sim;
4) pipe
1 library IEEE; 2 use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; 3 4 library work; 5 use work.my_components.all; 6 7 entity pipe is 8 port 9 ( 10 a, b, clk, rst: in std_logic; 11 q: out std_logic 12 ); 13 end pipe; 14 15 architecture sim of pipe is 16 signal s, cin, cout: std_logic; 17 begin 18 U1: component fau port map(a, b, cin, s, cout); 19 U2: component reg port map(cout, clk, rst, cin); 20 U3: component reg port map(s, clk, rst, q); 21 end sim;
5) my_components.vhd
1 library IEEE; 2 use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; 3 4 package my_components is 5 6 component and_2 is 7 port 8 ( 9 a, b: in std_logic; 10 y: out std_logic 11 ); 12 end component; 13 14 component fau is 15 port 16 ( 17 a, b, cin: in std_logic; 18 s, cout: out std_logic 19 ); 20 end component; 21 22 component reg is 23 port 24 ( 25 d, clk, rst: in std_logic; 26 q: out std_logic 27 ); 28 end component; 29 30 component pipe is 31 port 32 ( 33 a, b, clk, rst: in std_logic; 34 q: out std_logic 35 ); 36 end component; 37 38 end my_components;
6) multiplier.vhd
1 library IEEE; 2 use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; 3 4 library work; 5 use work.my_components.all; 6 7 entity multiplier is 8 port 9 ( 10 a, clk, rst: in std_logic; 11 b: in std_logic_vector(3 downto 0); 12 prod: out std_logic 13 ); 14 end multiplier; 15 16 architecture sim of multiplier is 17 signal and_out, reg_out: std_logic_vector(3 downto 0); 18 begin 19 U1: component and_2 port map(a, b(3), and_out(3)); 20 U2: component and_2 port map(a, b(2), and_out(2)); 21 U3: component and_2 port map(a, b(1), and_out(1)); 22 U4: component and_2 port map(a, b(0), and_out(0)); 23 U5: component reg port map(and_out(3), clk, rst, reg_out(3)); 24 U6: component pipe port map(and_out(2), reg_out(3), clk, rst, reg_out(2)); 25 U7: component pipe port map(and_out(1), reg_out(2), clk, rst, reg_out(1)); 26 U8: component pipe port map(and_out(0), reg_out(1), clk, rst, reg_out(0)); 27 28 prod <= reg_out(0); 29 30 end sim;
VHDL之Serial-Parallel Multiplier
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdie/p/4634586.html