标签:
本章将考察不同计算机(通过网络连接)上的进程相互通信的机制:网络进程间通信。
套接字描述符
正如使用文件描述符访问文件,应用程序用套接字描述符访问套接字。
许多处理文件描述符函数(如read和write)可以用于处理套接字描述符。调用socket函数创建一个套接字
#include <sys/socket.h> int socket(int domain,int type,int protocol);
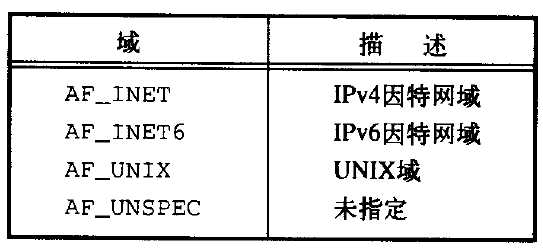
参数domain(域)确定通信的特性,包括地址格式。下图总结了POSIX.1指定的各个域,每个域都有自己表示地址的格式
参数type确定套接字的类型,下图总结了POSIX.1定义的套接字类型。

参数protocol通常是0,表示为给定的域和套接字类型选择默认协议。
调用socket与调用open相类似。可以调用close来关闭对文件或套接字的访问,并且释放该描述符以便重新使用。
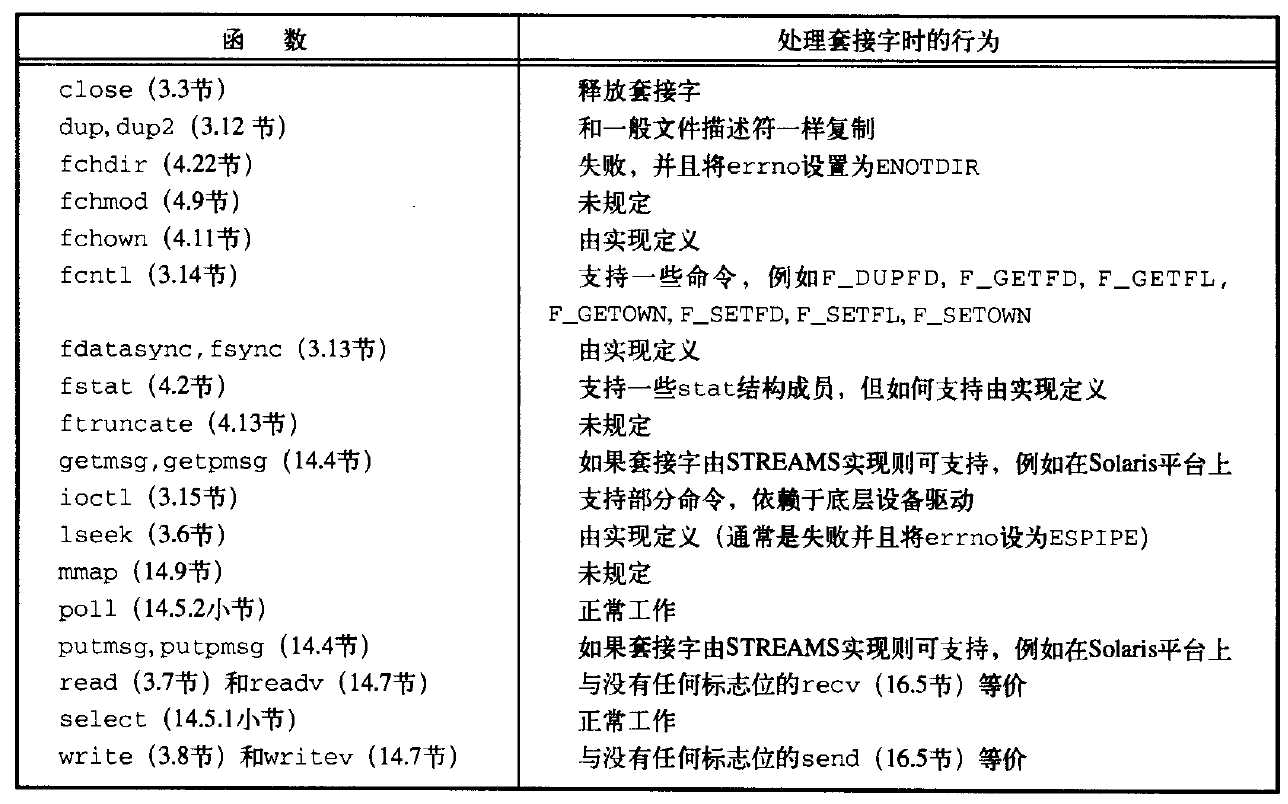
下图总结了到目前为止所讨论的大多数以文件描述符为参数的函数使用套接字描述符时的行为。
套接字通信是双向的。可以采用shutdown函数来禁止一个套接字的I/O
#include <sys/socket.h> int shutdown(int sockfd,int how);
如果how是SHUT_RD(关闭读端),那么无法从套接字读取数据。
如果how是SHUT_WR(关闭写端),那么无法使用套接字发送数据。
如果how是SHUT_RDWR,则既无法读取数据,又无法发送数据。
使用close函数直到关闭了最后一个引用它的文件描述符才会释放这个套接字,而shutdown允许使用一个套接字处于不活动状态,和引用它的文件描述符数目无关。
字节序
有4个用来处理处理器字节序和网络字节序之间实施转换的函数
#include <arpa/inet.h> uint32_t htonl(unit32_t hostint32); //返回值:以网络字节序表示的32位整数 uint16_t htons(unit16_t hostint16); //返回值:以网络字节序表示的16位整数 uint32_t ntohl(unit32_t netint32); //返回值:以主机字节序表示的32位整数 uint32_t ntons(unit16_t netint16); //返回值:以主机字节序表示的16位整数
地址格式
一个地址标识一个特定通信域的套接字端点,地址格式与这个特定的通信域相关。
为使不同的格式地址能够传入到套接字函数,地址会被强制转换成一个通用的地址结构sockaddr(Linux中的定义):
struct sockaddr{ sa_family_t sa_family; char sa_data[14]; };
因特网地址定义在<netinet/in.h>头文件中。在IPv4因特网域中,套接字地址用结构sockaddr_in表示:
struct in_addr{ in_addr_t s_addr; }; struct sockaddr_in{ sa_family_t sin_family; in_port_t sin_port; struct in_addr sin_addr; };
IPv6因特网域套接字地址用结构sockaddr_in6表示:
struct in6_addr{ uint8_t s6_addr[16]; }; struct sockaddr_in6{ sa_family_t sin6_family; in_port_t sin6_port; uint32_t sin6_flowinfo; struct in6_addr sin6_addr; uint32_t sin6_scope_id; };
下面两个函数用于二进制地址格式与十进制字符表示(a.b.c.d)之间的相互转换:
#include <arpa/inet.h> const char * inet_ntop (int domain, const void * restrict addr, char * restrict str, socklen_t size); int inet_pton ( int domain, const char * restrict str, void * restrict addr);
地址查询
通过调用gethostend,可以找到给定计算机系统的主机信息
#include <netdb.h> struct hostent *gethostent(void); void sethostent(int stayopen); void endhostent(void);
如果主机数据库文件没有打开,gethostent会打开它。函数gethostent返回文件中的下一个条目。
函数sethostent会打开文件,如果文件已经被打开,那么将其回绕。
hostent结构如下至少包含以下成员:
struct hostent { char *h_name; /* official name of host */ char **h_aliases; /* alias list */ int h_addrtype; /* host address type */ int h_length; /* length of address */ char **h_addr_list; /* list of addresses */ };
我们可以用以下函数在协议名字和协议编号之间进行映射:
#include <netdb.h> struct protoent *getprotobyname(const char *name); struct protoent *getprotobynumber(int proto); struct protoent *getprotoent(void); void setprotoent(int stayopen); void endprotoent(void);
POSIX.1定义的protoent结构至少包含以下成员:
struct protoent { char *p_name; /* official protocol name */ char **p_aliases; /* alias list */ int p_proto; /* protocol number */ };
可以使用函数getservbyname将一个服务名映射到一个端口号,使用函数getservbyport将一个端口号映射到一个服务名,使用函数getservent顺序扫描服务数据库
#include <netdb.h> struct servent *getservbyname(const char *name,const char *proto); struct servent *getservbyport(int port,const char *proto); struct servent *getservent(void); void setservent(int stayopen); void endservent(void);
servent结构至少包含以下成员:
struct servent { char *s_name; /* official service name */ char **s_aliases; /* alias list */ int s_port; /* port number */ char *s_proto; /* protocol to use */ };
POSIX.1定义了若干新的函数,允许一个应用程序将一个主机名和一个服务器名映射到一个地址
#include <sys/socket.h> #include <netdb.h> int getaddrinfo(const char *restrict host, const char *restrict service, const struct addrinfo *restrict hint, struct addrinfo **restrict res); void freeaddrinfo(struct addrinfo *ai);
需要提供主机名、服务名,或者两者都提供。函数返回一个链表结构addrinfo,可以用freeaddrinfo来释放一个或多个这种结构。
addrinfo结构的定义至少包含以下成员:
struct addrinfo { int ai_flags; int ai_family; int ai_socktype; int ai_protocol; socklen_t ai_addrlen; struct sockaddr *ai_addr; char *ai_canonname; struct addrinfo *ai_next; };
可以提供一个可选的hint来选择符合特定条件的地址。
如果getaddrinfo失败,需要调用gai_strerror将返回的错误码转换成错误消息
#include <netdb.h> const char *gai_strerror(int error);
getnameinfo函数将一个地址转换成一个主机名和一个服务名
#include <sys/socket.h> #include <netdb.h> int getnameinfo(const struct sockaddr *restrict addr,socklen_t alen, char *restrict host,socklen_t hostlen, char *restrict service,socklen_t servlen,int flags);
套接字地址被翻译为一个主机名和一个服务名。flags参数提供了一些控制翻译的方式,下图总结了支持的标志

下面程序说明了getaddrinfo函数的使用方法

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <arpa/inet.h> 5 #include <netdb.h> 6 #include <sys/socket.h> 7 8 void print_family(struct addrinfo *aip) 9 { 10 printf("family "); 11 switch(aip->ai_family) 12 { 13 case AF_INET: 14 printf("inet "); 15 break; 16 case AF_INET6: 17 printf("inet6 "); 18 break; 19 case AF_UNIX: 20 printf("unix "); 21 break; 22 case AF_UNSPEC: 23 printf("unspecified "); 24 break; 25 default: 26 printf("unkown "); 27 } 28 } 29 30 void print_type(struct addrinfo *aip) 31 { 32 printf("type "); 33 switch(aip->ai_socktype) 34 { 35 case SOCK_STREAM: 36 printf("stream "); 37 break; 38 case SOCK_DGRAM: 39 printf("datagram"); 40 break; 41 case SOCK_SEQPACKET: 42 printf("seqpacket "); 43 break; 44 case SOCK_RAW: 45 printf("raw "); 46 break; 47 default: 48 printf("unknown (%d)",aip->ai_socktype); 49 } 50 } 51 52 void print_protocol(struct addrinfo *aip) 53 { 54 printf(" protocol "); 55 switch(aip->ai_protocol) 56 { 57 case 0: 58 printf("default "); 59 break; 60 case IPPROTO_TCP: 61 printf("TCP "); 62 break; 63 case IPPROTO_UDP: 64 printf("UDP "); 65 break; 66 case IPPROTO_RAW: 67 printf("raw "); 68 break; 69 default: 70 printf("unknown (%d)",aip->ai_protocol); 71 } 72 } 73 74 void print_flags(struct addrinfo *aip) 75 { 76 printf("flags"); 77 if(aip->ai_flags == 0) 78 printf("0"); 79 else 80 { 81 if(aip->ai_flags & AI_PASSIVE) 82 printf(" passive "); 83 if(aip->ai_flags & AI_CANONNAME) 84 printf(" canon "); 85 if(aip->ai_flags & AI_NUMERICHOST) 86 printf(" numhost "); 87 } 88 } 89 90 int main() 91 { 92 struct addrinfo *ailist,*aip; 93 struct addrinfo hint; 94 struct sockaddr_in *sinp; 95 const char *addr; 96 int err; 97 char abuf[INET_ADDRSTRLEN]; 98 hint.ai_flags = AI_CANONNAME; 99 hint.ai_family = 0; 100 hint.ai_socktype = 0; 101 hint.ai_protocol = 0; 102 hint.ai_addrlen = 0; 103 hint.ai_canonname = NULL; 104 hint.ai_addr = NULL; 105 hint.ai_next = NULL; 106 if(getaddrinfo("localhost",NULL,&hint,&ailist) != 0) 107 { 108 printf("getaddrinfo error: %s",gai_strerror(err)); 109 exit(-1); 110 } 111 for(aip = ailist;aip != NULL;aip = aip->ai_next) 112 { 113 print_flags(aip); 114 print_family(aip); 115 print_type(aip); 116 print_protocol(aip); 117 printf("\n\thost %s",aip->ai_canonname ?aip->ai_canonname : "-"); 118 if(aip->ai_family == AF_INET) 119 { 120 sinp = (struct sockaddr_in *)aip->ai_addr; 121 addr = inet_ntop(AF_INET,&sinp->sin_addr,abuf,INET_ADDRSTRLEN); 122 printf(" address %s ",addr?addr:"unknown"); 123 printf(" port %d ",ntohs(sinp->sin_port)); 124 } 125 printf("\n"); 126 } 127 exit(0); 128 }
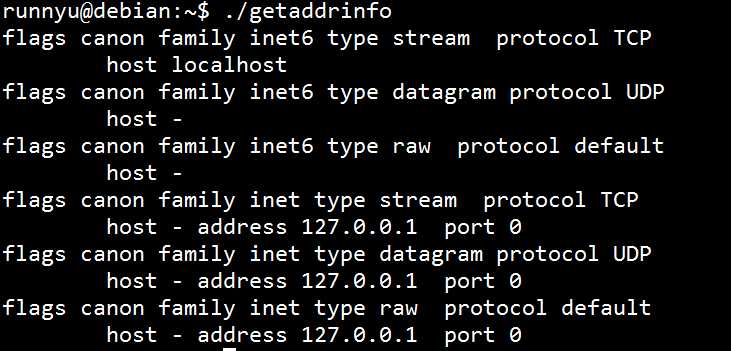
下面是程序运行结果
将套接字与地址关联
使用bind函数来关联地址和套接字
#include <sys/socket.h> int bind(int sockfd,const struct sockaddr *addr,socklen_t len);
可以调用getsockname函数来发现绑定到套接字上的地址
#include <sys/socket.h> int getsockname(int sockfd,struct sockaddr *restrict addr,socklen_t *restrict alenp);
如果套接字已经和对等方连接,可以调用getpeername函数找到对方的地址
#include <sys/socket.h> int getpeername(int sockfd,struct sockaddr *restrict addr,socklen_t *restrict alenp);
建立连接
如果处理一个面向连接的网络服务,那么开始交换数据之前,需要使用connect函数来建立连接
#include <sys/socket.h> int connect(int sockfd,const struct sockaddr *addr,socklen_t len);
connect中指定的地址是我们想与之通信的服务器地址。
服务器调用listen函数来宣告它愿意接受连接请求
#include <sys/socket.h> int listen(int sockfd,int backlog);
参数backlog提供了一个提示,提示系统改进程所要入队的未完成连接请求数量。一旦队列满了,系统就会拒绝多余的连接请求。
一旦服务器调用了listen,所用的套接字就恩能够接受连接请求。使用accept函数获得连接请求并建立连接。
#include <sys/socket.h> int accept(int fd,struct sockaddr *restrict addr,socklen_t *restrict len);
函数返回的是一个连接到调用connect的客户端的套接字描述符
数据传输
在建立了连接之后,就可以使用read和write来通过套接字通信。
除此之外,有6个位数据传递而设计的套接字函数(3个用于发送数据,3个用于接收数据)。
最简单的是send,它和write很像,但是可以指定标志来改变处理传输数据的方式
#include <sys/socket.h> ssize_t send(int sockfd,const void *buf,size_t nbytes,int flags);
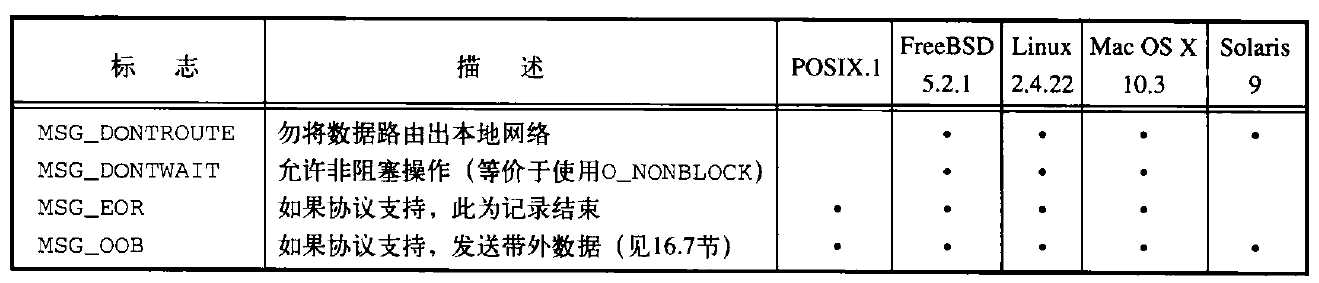
下面总结了flags可能的取值
函数sendto和send很类似,区别在于sendto可以在无连接的套接字上指定一个目标地址
#include <sys/socket.h> ssize_t sendto(int sockfd,const void *buf,size_t nbytes,int flags, const struct sockaddr *destaddr,socklen_t destlen);
对于面向连接的套接字,目标地址是被忽略的。
通过套接字发送数据时,还有一个选择。可以调用带有msghdr结构的sendmsg来指定多重缓冲区传输数据。
#include <sys/socket.h> ssize_t sendmsg(int sockfd,const struct msghdr *msg,int flags);
POSIX.1定义了msghdr结构,它至少有以下成员:
struct msghdr { void *msg_name; /* optional address */ socklen_t msg_namelen; /* size of address */ struct iovec *msg_iov; /* scatter/gather array */ size_t msg_iovlen; /* # elements in msg_iov */ void *msg_control; /* ancillary data, see below */ size_t msg_controllen; /* ancillary data buffer len */ int msg_flags; /* flags on received message */ };
函数recv和read相似,但是recv可以指定标志来控制如何接收数据
#include <sys/socket.h> ssize_t recv(int sockfd,void *buf,size_t nbytes,int flags);
下图总结了这些标志
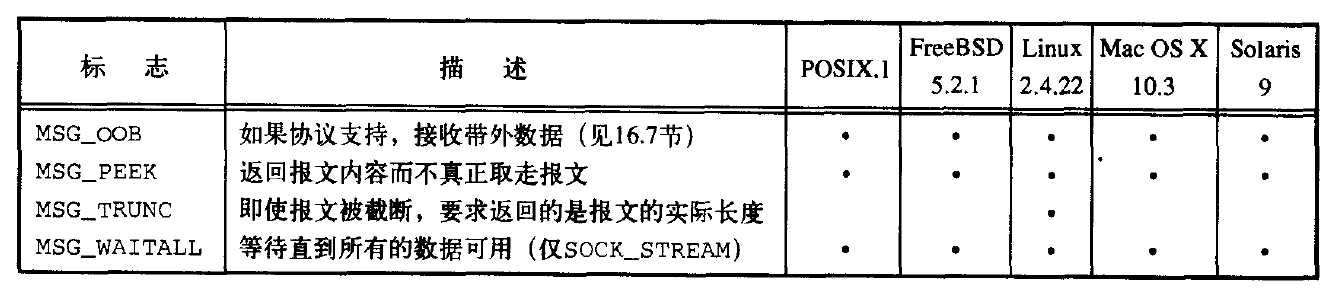
如果有兴趣定位发送者,可以使用recvfrom来得到数据发送者的源地址
#include <sys/socket.h> ssize_t recvfrom(int sockfd,void *restrict buf,size_t len,int flags struct sockaddr *restrict addr, socklen_t *restrict addrlen);
如果addr非空,它将包含数据发送者的套接字端点地址。通常用于无连接的套接字。
为了将接收到的数据送入多个缓冲区,或者想接收辅助数据,可以使用recvmsg
#include <sys/socket.h> ssize_t recvmsg(int sockfd,struct msghdr *msg,int flags);
返回时,msghdr结构中的msg_flags字段都被设为所接收数据的特征。
面向连接实例
下面程序显示了一个与服务器通信的客户端从系统的uptime命令获得输出。

1 #include "apue.h" 2 #include <netdb.h> 3 #include <errno.h> 4 #include <sys/socket.h> 5 6 #define BUFLEN 128 7 8 extern int connect_retry(int, int, int, const struct sockaddr *, 9 socklen_t); 10 11 void 12 print_uptime(int sockfd) 13 { 14 int n; 15 char buf[BUFLEN]; 16 17 while ((n = recv(sockfd, buf, BUFLEN, 0)) > 0) 18 write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n); 19 if (n < 0) 20 err_sys("recv error"); 21 } 22 23 int 24 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 25 { 26 struct addrinfo *ailist, *aip; 27 struct addrinfo hint; 28 int sockfd, err; 29 30 if (argc != 2) 31 err_quit("usage: ruptime hostname"); 32 memset(&hint, 0, sizeof(hint)); 33 hint.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; 34 hint.ai_canonname = NULL; 35 hint.ai_addr = NULL; 36 hint.ai_next = NULL; 37 if ((err = getaddrinfo(argv[1], "ruptime", &hint, &ailist)) != 0) 38 err_quit("getaddrinfo error: %s", gai_strerror(err)); 39 for (aip = ailist; aip != NULL; aip = aip->ai_next) { 40 if ((sockfd = connect_retry(aip->ai_family, SOCK_STREAM, 0, 41 aip->ai_addr, aip->ai_addrlen)) < 0) { 42 err = errno; 43 } else { 44 print_uptime(sockfd); 45 exit(0); 46 } 47 } 48 err_exit(err, "can‘t connect to %s", argv[1]); 49 }
这个程序连接服务器,读取服务器发送过来的字符串并将其打印到标准输出。
下面展示了服务器程序,用来提供uptime命令的输出到上面的客户端程序

1 #include "apue.h" 2 #include <netdb.h> 3 #include <errno.h> 4 #include <syslog.h> 5 #include <sys/socket.h> 6 7 #define BUFLEN 128 8 #define QLEN 10 9 10 #ifndef HOST_NAME_MAX 11 #define HOST_NAME_MAX 256 12 #endif 13 14 extern int initserver(int, const struct sockaddr *, socklen_t, int); 15 16 void 17 serve(int sockfd) 18 { 19 int clfd; 20 FILE *fp; 21 char buf[BUFLEN]; 22 23 set_cloexec(sockfd); 24 for (;;) { 25 if ((clfd = accept(sockfd, NULL, NULL)) < 0) { 26 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: accept error: %s", 27 strerror(errno)); 28 exit(1); 29 } 30 set_cloexec(clfd); 31 if ((fp = popen("/usr/bin/uptime", "r")) == NULL) { 32 sprintf(buf, "error: %s\n", strerror(errno)); 33 send(clfd, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 34 } else { 35 while (fgets(buf, BUFLEN, fp) != NULL) 36 send(clfd, buf, strlen(buf), 0); 37 pclose(fp); 38 } 39 close(clfd); 40 } 41 } 42 43 int 44 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 45 { 46 struct addrinfo *ailist, *aip; 47 struct addrinfo hint; 48 int sockfd, err, n; 49 char *host; 50 51 if (argc != 1) 52 err_quit("usage: ruptimed"); 53 if ((n = sysconf(_SC_HOST_NAME_MAX)) < 0) 54 n = HOST_NAME_MAX; /* best guess */ 55 if ((host = malloc(n)) == NULL) 56 err_sys("malloc error"); 57 if (gethostname(host, n) < 0) 58 err_sys("gethostname error"); 59 daemonize("ruptimed"); 60 memset(&hint, 0, sizeof(hint)); 61 hint.ai_flags = AI_CANONNAME; 62 hint.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; 63 hint.ai_canonname = NULL; 64 hint.ai_addr = NULL; 65 hint.ai_next = NULL; 66 if ((err = getaddrinfo(host, "ruptime", &hint, &ailist)) != 0) { 67 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: getaddrinfo error: %s", 68 gai_strerror(err)); 69 exit(1); 70 } 71 for (aip = ailist; aip != NULL; aip = aip->ai_next) { 72 if ((sockfd = initserver(SOCK_STREAM, aip->ai_addr, 73 aip->ai_addrlen, QLEN)) >= 0) { 74 serve(sockfd); 75 exit(0); 76 } 77 } 78 exit(1); 79 }
另一个版本的服务器程序

1 #include "apue.h" 2 #include <netdb.h> 3 #include <errno.h> 4 #include <syslog.h> 5 #include <fcntl.h> 6 #include <sys/socket.h> 7 #include <sys/wait.h> 8 9 #define QLEN 10 10 11 #ifndef HOST_NAME_MAX 12 #define HOST_NAME_MAX 256 13 #endif 14 15 extern int initserver(int, const struct sockaddr *, socklen_t, int); 16 17 void 18 serve(int sockfd) 19 { 20 int clfd, status; 21 pid_t pid; 22 23 set_cloexec(sockfd); 24 for (;;) { 25 if ((clfd = accept(sockfd, NULL, NULL)) < 0) { 26 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: accept error: %s", 27 strerror(errno)); 28 exit(1); 29 } 30 if ((pid = fork()) < 0) { 31 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: fork error: %s", 32 strerror(errno)); 33 exit(1); 34 } else if (pid == 0) { /* child */ 35 /* 36 * The parent called daemonize ({Prog daemoninit}), so 37 * STDIN_FILENO, STDOUT_FILENO, and STDERR_FILENO 38 * are already open to /dev/null. Thus, the call to 39 * close doesn‘t need to be protected by checks that 40 * clfd isn‘t already equal to one of these values. 41 */ 42 if (dup2(clfd, STDOUT_FILENO) != STDOUT_FILENO || 43 dup2(clfd, STDERR_FILENO) != STDERR_FILENO) { 44 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: unexpected error"); 45 exit(1); 46 } 47 close(clfd); 48 execl("/usr/bin/uptime", "uptime", (char *)0); 49 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: unexpected return from exec: %s", 50 strerror(errno)); 51 } else { /* parent */ 52 close(clfd); 53 waitpid(pid, &status, 0); 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 58 int 59 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 60 { 61 struct addrinfo *ailist, *aip; 62 struct addrinfo hint; 63 int sockfd, err, n; 64 char *host; 65 66 if (argc != 1) 67 err_quit("usage: ruptimed"); 68 if ((n = sysconf(_SC_HOST_NAME_MAX)) < 0) 69 n = HOST_NAME_MAX; /* best guess */ 70 if ((host = malloc(n)) == NULL) 71 err_sys("malloc error"); 72 if (gethostname(host, n) < 0) 73 err_sys("gethostname error"); 74 daemonize("ruptimed"); 75 memset(&hint, 0, sizeof(hint)); 76 hint.ai_flags = AI_CANONNAME; 77 hint.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; 78 hint.ai_canonname = NULL; 79 hint.ai_addr = NULL; 80 hint.ai_next = NULL; 81 if ((err = getaddrinfo(host, "ruptime", &hint, &ailist)) != 0) { 82 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: getaddrinfo error: %s", 83 gai_strerror(err)); 84 exit(1); 85 } 86 for (aip = ailist; aip != NULL; aip = aip->ai_next) { 87 if ((sockfd = initserver(SOCK_STREAM, aip->ai_addr, 88 aip->ai_addrlen, QLEN)) >= 0) { 89 serve(sockfd); 90 exit(0); 91 } 92 } 93 exit(1); 94 }
无连接的实例
下面程序采用数据报套接字接口的uptime客户端命令版本

1 #include "apue.h" 2 #include <netdb.h> 3 #include <errno.h> 4 #include <sys/socket.h> 5 6 #define BUFLEN 128 7 #define TIMEOUT 20 8 9 void 10 sigalrm(int signo) 11 { 12 } 13 14 void 15 print_uptime(int sockfd, struct addrinfo *aip) 16 { 17 int n; 18 char buf[BUFLEN]; 19 20 buf[0] = 0; 21 if (sendto(sockfd, buf, 1, 0, aip->ai_addr, aip->ai_addrlen) < 0) 22 err_sys("sendto error"); 23 alarm(TIMEOUT); 24 if ((n = recvfrom(sockfd, buf, BUFLEN, 0, NULL, NULL)) < 0) { 25 if (errno != EINTR) 26 alarm(0); 27 err_sys("recv error"); 28 } 29 alarm(0); 30 write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n); 31 } 32 33 int 34 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 35 { 36 struct addrinfo *ailist, *aip; 37 struct addrinfo hint; 38 int sockfd, err; 39 struct sigaction sa; 40 41 if (argc != 2) 42 err_quit("usage: ruptime hostname"); 43 sa.sa_handler = sigalrm; 44 sa.sa_flags = 0; 45 sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask); 46 if (sigaction(SIGALRM, &sa, NULL) < 0) 47 err_sys("sigaction error"); 48 memset(&hint, 0, sizeof(hint)); 49 hint.ai_socktype = SOCK_DGRAM; 50 hint.ai_canonname = NULL; 51 hint.ai_addr = NULL; 52 hint.ai_next = NULL; 53 if ((err = getaddrinfo(argv[1], "ruptime", &hint, &ailist)) != 0) 54 err_quit("getaddrinfo error: %s", gai_strerror(err)); 55 56 for (aip = ailist; aip != NULL; aip = aip->ai_next) { 57 if ((sockfd = socket(aip->ai_family, SOCK_DGRAM, 0)) < 0) { 58 err = errno; 59 } else { 60 print_uptime(sockfd, aip); 61 exit(0); 62 } 63 } 64 65 fprintf(stderr, "can‘t contact %s: %s\n", argv[1], strerror(err)); 66 exit(1); 67 }
下面是对应的服务器版本

1 #include "apue.h" 2 #include <netdb.h> 3 #include <errno.h> 4 #include <syslog.h> 5 #include <sys/socket.h> 6 7 #define BUFLEN 128 8 #define MAXADDRLEN 256 9 10 #ifndef HOST_NAME_MAX 11 #define HOST_NAME_MAX 256 12 #endif 13 14 extern int initserver(int, const struct sockaddr *, socklen_t, int); 15 16 void 17 serve(int sockfd) 18 { 19 int n; 20 socklen_t alen; 21 FILE *fp; 22 char buf[BUFLEN]; 23 char abuf[MAXADDRLEN]; 24 struct sockaddr *addr = (struct sockaddr *)abuf; 25 26 set_cloexec(sockfd); 27 for (;;) { 28 alen = MAXADDRLEN; 29 if ((n = recvfrom(sockfd, buf, BUFLEN, 0, addr, &alen)) < 0) { 30 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: recvfrom error: %s", 31 strerror(errno)); 32 exit(1); 33 } 34 if ((fp = popen("/usr/bin/uptime", "r")) == NULL) { 35 sprintf(buf, "error: %s\n", strerror(errno)); 36 sendto(sockfd, buf, strlen(buf), 0, addr, alen); 37 } else { 38 if (fgets(buf, BUFLEN, fp) != NULL) 39 sendto(sockfd, buf, strlen(buf), 0, addr, alen); 40 pclose(fp); 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 45 int 46 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 47 { 48 struct addrinfo *ailist, *aip; 49 struct addrinfo hint; 50 int sockfd, err, n; 51 char *host; 52 53 if (argc != 1) 54 err_quit("usage: ruptimed"); 55 if ((n = sysconf(_SC_HOST_NAME_MAX)) < 0) 56 n = HOST_NAME_MAX; /* best guess */ 57 if ((host = malloc(n)) == NULL) 58 err_sys("malloc error"); 59 if (gethostname(host, n) < 0) 60 err_sys("gethostname error"); 61 daemonize("ruptimed"); 62 memset(&hint, 0, sizeof(hint)); 63 hint.ai_flags = AI_CANONNAME; 64 hint.ai_socktype = SOCK_DGRAM; 65 hint.ai_canonname = NULL; 66 hint.ai_addr = NULL; 67 hint.ai_next = NULL; 68 if ((err = getaddrinfo(host, "ruptime", &hint, &ailist)) != 0) { 69 syslog(LOG_ERR, "ruptimed: getaddrinfo error: %s", 70 gai_strerror(err)); 71 exit(1); 72 } 73 for (aip = ailist; aip != NULL; aip = aip->ai_next) { 74 if ((sockfd = initserver(SOCK_DGRAM, aip->ai_addr, 75 aip->ai_addrlen, 0)) >= 0) { 76 serve(sockfd); 77 exit(0); 78 } 79 } 80 exit(1); 81 }
套接字选项
套接字机制提供了设置跟查询套接字选项的接口。可以获取或设置以下3种选项
1.通用选项,工作在所有套接字类型上
2.在套接字层次管理的选项,但是依赖于下层协议的支持
3.特定于某协议的选项,每个协议独有的
可以使用setsockopt函数来设置套接字选项
#include <sys/socket.h> int setsockopt(int sockfd,int level,int option,const void *val,socklen_t len);
level标识了选项应用的协议:
如果选项是通用的套接字层次选项,则level设置为SOL_SOCKET,否则,level设置成控制这个选项的协议编号。对于TCP选项,level是IPPROTO_TCP,对于IP,level是IPPROTO_IP。
下面总结了Single UNIX Specification中定义的通用套接字层次选项
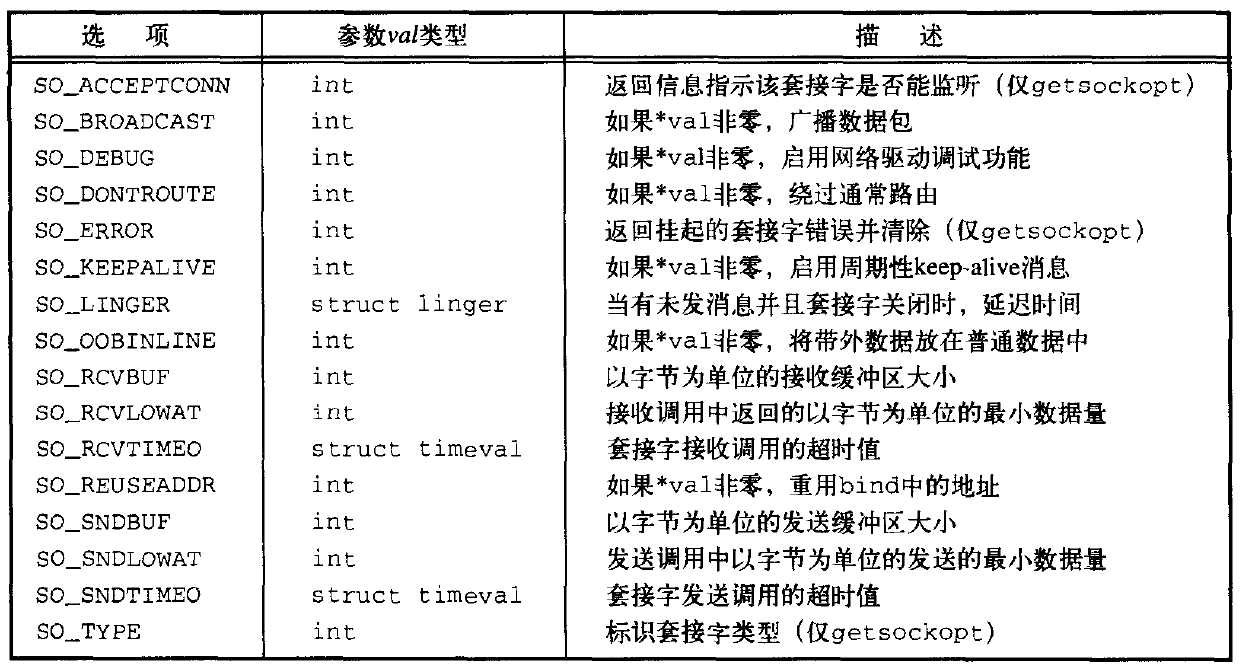
可以使用getsockopt函数来查看选项的当前值
#include <sys/socket.h> int getsockopt(int sockfd,int level,int option,void *restrict val,socklen_t restrict lenp);
带外数据
带外数据是一些通信协议所支持的可选特征,允许更加高级的数据比普通数据优先传输。
TCP将带外数据称为紧急数据。TCP仅支持一个字节的紧急数据,但是允许紧急数据在普通数据传递机制数据流之外传输。
为了产生紧急数据,在三个send函数中任何一个指定标志MSG_OOB。如果带MSG_OOB标志传输字节超过一个时,最后一个字节被作为紧急数据字节。
如果安排发生套接字信号,当接收到紧急数据时,那么发送信号SIGURG信号。可以通过调用以下函数安排进程接收套接字的信号:
fcntl(sockfd,F_SETTOWN,pid);
F_GETOWN命令可以用来获取当前套接字所有权
owner=fcntl(sockfd,F_GETOWN,0);
为帮助判断是否已经达到紧急标记,可以使用函数sockatmark
#include <sys/socket.h> int sockatmark(int sockfd);
当下一个要读取的字节在紧急标志处时,sockatmark返回1。
非阻塞和异步I/O
在基于套接字异步I/O中,当能够从套接字中读取数据,或者套接字写队列中的空间变得可用时,可以安排发送信号SIGIO。通过两个步骤来使用异步I/O:
1) 建立套接字拥有者关系,信号可以被传送到合适的进程。
2) 通知套接字当I/O操作不会阻塞时发信号告知。
可以使用三种方式来完成第一个步骤:
A、 在fcntl使用F_SETOWN命令
B、 在ioctl中作用FIOSETOWN命令
C、 在ioctl中使用SIOCSPGRP命令。
要完成第二个步骤,有两个选择:
A、 在fcntl中使用F_SETFL命令并且启用文件标志O_ASYNC。
B、 在ioctl中使用FIOASYNC
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/runnyu/p/4648678.html