标签:
关于Objective-C 的property,很多iOS开发的新手都会很迷惑,也会包括有经验的iOS开发程序员,
因为Objective-C的property,说多不多,说少却也不少,从MRR(Manual Retain Release )到ARC模式,很多属性功能类似
名称却不一样,比如strony和retain,而且又牵扯到release, autorelease, alloc ,new,copy等一众函数,
所以看着很容被绕进去,迷失在这众多的property,
今天特地梳理支持ARC(iOS 5+) 的propterty的关键词:
strong, weak, copy, readonly/readwrite, atomic/nonatomic,assign,retain
由于strong和retain功能相同,所以会在最后总结的时候,比较所有的这些关键词异同点
1:定义一个property
如下,我们定义一个car 的interface, 该属性有一个property 为 brand(品牌)
// Car.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface Car : NSObject @property NSString *brand; @end
// Car.m #import "Car.h" @implementation car @synthesize brand = _brand; @end
2:属性的getter 和setter方法和synthesize
编译器会默认的为属性生成getter 和setter方法
- (NSString *)brand { return _brand;//_brand即使synthesize指定的属性名称 } - (void)setBrand:(NSString *)brand { _brand = brand; }
注意:synthesize 不是必须明确声明,除非手动些属性的getter和setter方法
否则,complier默认生成的code 如下格式
@synthesize brand = _brand
synthesize关键字缺省方式是:将brand属性对应的实例便令声明为_brand,即_ + propertyname
当然可以自己指定比如brand = xxxbrand
编译器默认会将getter方法和属性同名,setter方法为set+属性(首字母大写),例如setBrand
可以指定属性的getter和setter方法名称
@property (nonatomic,getter=getBrand, setter = setBrand:)NSString *brand;
3:readonly和readwrite
声明 readonly属性
@property (readonly,getter=getBrand)NSString *brand;
声明了readonly的属性,一定没有setter方法,所以你可以使用getter或者 dot方法 获取属性的值,但肯定不可以使用
setter方法修改
Car *c = [[Car alloc]init];0 [c setBrand:@"tony"]; //Error NSLog(@"%@", [c getBrand]);
声明为readonly 不意味着我们不可以修改,propery 的accessor method 本来就是提供给其他接口调用的,
在我们内部,是直接操纵_brand实例的, 如下
// Car.h
- (void)setBrand:(NSString *)brand;
// Car.m
- (void )setBrand:(NSString *)brand; { _brand = brand; }
readonly 对应的readwrite 属性, readwrite 是default的behavior,可以不显示声明
@property (readwrite)NSString *brand;
4:atomic, nonatomic
atomic 原子的,default behavior,支持多线程操作, 代价是开销比nonatomic大
如果声明一个属性,确定不会运行在多线程的环境,可以直接声明为nonatomic
@property (nonatomic)NSString *brand;
内存管理
Ojective-C 内存模型中,不管是MRR,还是ARC,都是根据对象的引用计数来确定对象是否回收
当对象的 引用计数为0,就会被回收(不一定是立即回收)
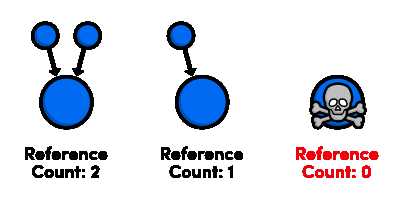
从引用计数的原理出发,Objective-C 提出了三种相关的是属性
strong, weak, copy
1:strony 属性
strong属性,即声明一个对象拥有另外一个对象,引用计数 + 1
加入 A对象 有个strong 属性的实例对象B, 则在A对象释放之前,B是不会释放的
看如下sample code
声明一个类Person,Person有一个属性name
// // Person.h #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface Person : NSObject @property (nonatomic) NSString *name; @end
// Person.m #import "Person.h" @implementation Person - (NSString *)description { return self.name; } @end
声明一个Car 类,有两个属性 model和driver
// Car.h #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Person.h" @interface Car : NSObject @property (nonatomic) NSString *model; @property (nonatomic,strong) Person *driver; @end
main.m
// main.m #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Car.h" #import "Person.h" int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { Person *john = [[Person alloc] init]; john.name = @"John"; Car *honda = [[Car alloc] init]; honda.model = @"Honda Civic"; honda.driver = john; NSLog(@"%@ is driving the %@", honda.driver, honda.model); } return 0; }
可以看到,hoda对象对driver对象负责
2:weak属性
strong 属性,很直观的显示对象直接的关系,但也很容易引起内存泄露,
看如下代码,我们稍微小改了Person.h ,增加了Car 属性,
// Person.h #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @class Car; @interface Person : NSObject @property (nonatomic) NSString *name; @property (nonatomic, strong) Car *car; @end
则在main.m
增加一行
john.car = honda;
则此时,john和hoda互相持有对方
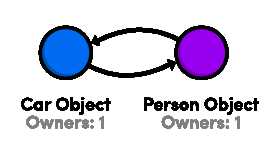
二者这件形成了 retain cycle(互相持有的循环),就是典型的内存泄露的一种情况
如果car声明为weak,这个问题即迎刃而解
@property (nonatomic, weak) Car *car;
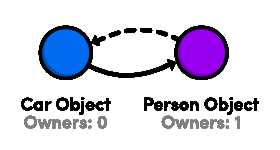
3:copy 属性
copy不同于strong, 并不拥有copy的对象,而是复制该对象(必须conform NSCopying protocol )
sample code
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Car.h" #import "Person.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { Car *bmw = [[Car alloc]init]; Person *driver = [[Person alloc]init]; NSMutableString *name = [NSMutableString stringWithFormat:@"zhangsan"];//mutable 的name 为zhangsan [driver setName:name]; [name setString:@"lisi"];//修改为lisi [driver setCar:bmw]; [bmw setModel:@"X5"]; [bmw setDriver:driver]; NSLog(@"%@", [driver name]);//仍然是zhangsan }
copy 属性在被赋值的时候就copy了该值,所以即使该值是mutable的,属性的值也不会被修改,
现对于strong的持有对象,copy特别适合只是简单存储值得属性
以上都是ARC支持的属性。
4:属性retain
等同于 strong
5:unsafe_unretained
类似于weak,和weak不同的是,如果weak 属性指向的对象如果被销毁后,weak 属性被置为nil,
而 unsafe_unretained 不会,则又可能形成悬垂指针的问题
6:assign
默认的属性,不需要显示声明
指定setter方法进行简单的赋值 ,对基础数据类型(NSInteger,CGFloat)
和C数据类型(int, float, double, char)等等。
总结:
atomic //default
nonatomic
strong=retain //default
weak
assign //default
unsafe_unretained
copy
readonly
readwrite //default
引用:
http://rypress.com/tutorials/objective-c/properties
http://rypress.com/tutorials/objective-c/memory-management
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/8927727/objective-c-arc-strong-vs-retain-and-weak-vs-assign
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/geeker/p/4677519.html