标签:
一、抽象类
抽象类是用abstract修饰的类,关于这一点,个人认为要强调一下的是抽象类中不一定要有抽象方法。
1.最常见的抽象类形式
1 package com.proxy; 2 3 public abstract class Super { 4 public abstract void f(); 5 6 }
抽象类用abstract修饰,抽象方法也是用abstract修饰并且不能有{}
2.很多书籍都会关注抽象类和抽象方法之间的关系,但是抽象类的存在,并不由是否存在抽象方法决定:
1 package com.proxy; 2 3 public abstract class Super { 4 public void f() { 5 System.out.println("测试"); 6 } 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Super s = new Super() { 10 11 }; 12 13 s.f(); 14 } 15 }
结果如下:
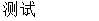
这里注意,虽然没有抽象方法,但是抽象类还是不能直接new Super()的形式,需要使用 new Super(){}
3.抽象类中可以存在非抽象的方法
4.子类继承一个抽象类,需要实现其中的抽象方法,但是只有全部的抽象方法全部实现的时候这个子类才能成为一个普通类,否则这个子类也会是抽象类
5.对于类而言,抽象与否与是否static没有直接关系
1 package com.proxy; 2 3 public abstract class Super { 4 public static void f() { 5 System.out.println("测试"); 6 } 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Super.f(); 10 } 11 }
在这个问题上,个人觉得可以这么理解,用abstract修饰类,决定的是能否new 的方式直接创建, 而static是属于类的,不需要创建对象就能够存在,所以不要混淆抽象类和static
二、接口
接口可以认为是特殊的抽象类,它们都是“类级别”的, 接口使用interface ,与抽象类不同的是里面如果有方法,则必须是抽象方法
1.接口中可以没有任何方法
1 public interface Super {}
更常见的一个没有任何方法的接口就是java.io.Serializable
2.接口默认权限是public,抽象类的默认权限还是default,但是这句话说的是“方法”, 之前介绍权限的章节中曾经提到过: 方法可以用public,private,protected,default来修饰,但是类只能用public ,default修饰
接口作为“类级别的”,同样只能够用public,default来修饰,而且接口并不遵循“默认权限是public”的规则
见下例:
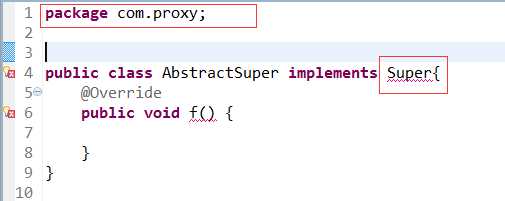
这里接口没有声明public,在包外就访问不到了。
推荐的做法:不管是interface,还是接口中的方法,都写上public
3.接口中的数据必须是常量 public static final int i=1;这种形式(并且默认就是static final的), 注意常量在使用前必须初始化值
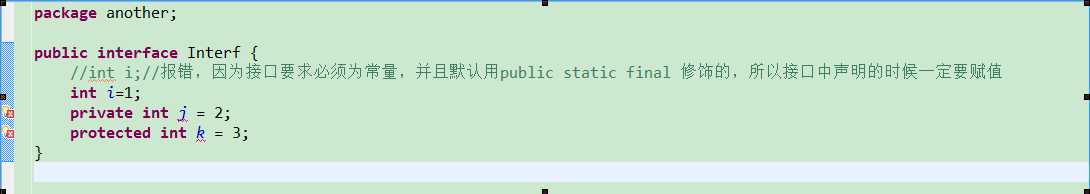
注意,不能用private,protected来修饰接口中的常量
4.接口声明能够指向任何的实现这个接口的类
这是非常重要的一个特性,它类似于父类声明指向子类对象,但是又是在这个的基础上面的拓展,进一步方便我们在设计的时候解耦
可以参考四(2)的章节,里面动态代理就是基于此的。java中关于这一点,专业地称为:通过接口来实现完全解耦。
介绍到接口来实现完全解耦,另一个很有名的用法,就是策略模式,适配器模式的实现,关于策略模式、适配器详解参考将在下两篇文章中给出。
三、接口的多继承
java中的类,只支持单继承,但是接口却能够支持多继承(实现),见下例:
1 package another; 2 3 public interface Interf1 { 4 public void f1(); 5 } 6 7 8 9 package another; 10 11 public interface Interf2 { 12 public void f2(); 13 } 14 15 16 17 package another; 18 19 public class MultiInterfacesTest implements Interf1,Interf2{ 20 public void f1() { 21 System.out.println("f1"); 22 } 23 24 public void f2() { 25 System.out.println("f2"); 26 } 27 28 public static void main(String[]args) { 29 MultiInterfacesTest t = new MultiInterfacesTest(); 30 t.f1(); 31 t.f2(); 32 } 33 }
结果如下:

注意:如果要同时继承某个类并且实现接口,需要写成public class Sub extends Super implements Intf {} 的形式
最后,考虑一下接口的设计原因:
第一、能够方便程序向上转型,完全解耦
第二、实现更好的“边界”,A、B两个程序员交互可以直接通过接口
四、通过继承来拓展接口
1.类可以extends来实现类之间的继承,接口也可以通过extends 来实现接口之间的继承
1 package another; 2 3 public interface Interf1 { 4 public void f1(); 5 } 6 7 8 package another; 9 10 public interface Interf2 extends Interf1{//接口之间的继承 11 public void f2(); 12 } 13 14 15 package another; 16 17 public class MultiInterfacesTest implements Interf2{ 18 public void f1() { 19 System.out.println("f1"); 20 } 21 22 public void f2() { 23 System.out.println("f2"); 24 } 25 26 public static void main(String[]args) { 27 MultiInterfacesTest t = new MultiInterfacesTest(); 28 t.f1(); 29 t.f2(); 30 } 31 }
结果如下:

2.正如上面所说的,接口可以继承接口,那么如果碰到子类接口和父类接口重名的情况会怎么样?
1 package com.proxy; 2 3 public interface Interf1 { 4 public void f1(); 5 } 6 7 8 package com.proxy; 9 10 public interface Interf2 extends Interf1{ 11 @Override 12 public void f1(); 13 } 14 15 package com.proxy; 16 17 public class Test implements Interf2{ 18 @Override 19 public void f1() { 20 System.out.println("测试"); 21 } 22 23 public static void main(String[] args) { 24 Test test = new Test(); 25 test.f1(); 26 } 27 }
结果如下:

子类接口和父类接口方法相同,其实跟类是一样的,发生覆盖; 如果方法名相同参数等不同,则发生重载
3.如果多个接口含有相同方法
1 package com.proxy; 2 3 public interface Interf1 { 4 public void f1(); 5 } 6 7 package com.proxy; 8 9 public interface Interf2 { 10 public void f1(); 11 } 12 13 package com.proxy; 14 15 public class Test implements Interf1,Interf2{//实现的两个接口中有相同的方法 16 @Override 17 public void f1() { 18 System.out.println("测试"); 19 } 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 Test test = new Test(); 23 test.f1(); 24 } 25 }
结果如下:

按照上面的写法,虽然实现一次f1() 不会报错,但是不推荐这样的情况
4.小心接口重名但是不能构成重载条件,见下例:
1 package com.proxy; 2 3 public interface Interf1 { 4 public Integer f1();//Integer返回值 5 } 6 7 8 package com.proxy; 9 10 public interface Interf2 { 11 public void f1();// void 12 } 13 14 15 package com.proxy; 16 17 public class Test implements Interf1,Interf2{ 18 @Override 19 public void f1() {//这里直接报错 20 System.out.println("f1"); 21 } 22 public static void main(String[]args) { 23 Test t = new Test(); 24 t.f1(); 25 } 26 }
这里直接编译报错
这里两个接口中有相同的方法f1(),但是仅仅是返回值不同,不能够构成重载条件,在实现方法的时候编译器不能区分到底实现的是哪个方法,所以编译报错
编写接口的时候尽量不要重名
五、嵌套接口
1.接口定义在类中
1 package pack; 2 3 public class A { 4 interface B {//在类中声明接口 5 void b(); 6 } 7 8 public interface C {//类中的接口声明为public 9 void c() ; 10 } 11 12 private interface D { //类中的接口声明为private,之前提过,类不能够采用protected,default,private 修饰 13 //其实不太准确,应该是写在最外面层级的类不能,写在某个类里面的接口、类,它们的级别和普通方法是一样的 14 //它们可以用private,protected,default,public 修饰. 注意,连public都可以,最外层的类只能有一个public, 15 //放在类中的 是方法级别的类、接口, 同样可以用public修饰 16 void d(); 17 } 18 19 20 protected interface E { 21 void e(); 22 } 23 24 25 26 class ImplB implements B { 27 @Override 28 public void b() { 29 System.out.println("实现B接口"); 30 } 31 } 32 33 public class ImplC implements C { 34 @Override 35 public void c() { 36 System.out.println("实现C接口"); 37 } 38 } 39 40 private class ImplD implements D { 41 @Override 42 public void d() { 43 System.out.println("实现D接口"); 44 } 45 } 46 47 48 protected class ImplE implements E { 49 @Override 50 public void e() { 51 System.out.println("实现E接口"); 52 } 53 } 54 55 56 public static void main(String[]args){ 57 A a = new A(); 58 ImplB bb = a.new ImplB(); 59 ImplC cc = a.new ImplC(); 60 ImplD dd = a.new ImplD(); 61 ImplE ee = a.new ImplE(); 62 63 bb.b(); 64 cc.c(); 65 dd.d(); 66 ee.e(); 67 } 68 }
结果如下:

2.接口定义在接口中
1 package pack; 2 3 public interface InnerInterface { 4 interface innerDefault { 5 void f1(); 6 } 7 8 // protected interface innerProtected { //报错,这里也是方法级别的 ,为什么不能用protected,private呢? 9 //因为接口里面的方法级别也只能用public修饰啊!!!接口和类不同,别弄混了。默认就是public 10 // void f2(); 11 // } 12 // 13 // private interface innerPrivate { 14 // 15 // } 16 17 // prviate void ff();// 这里报错,方法级别不能用private修饰,因为用了就不能被覆盖实现,所以肯定不行 18 19 public void f2(); 20 } 21 22 23 package pack; 24 25 public class Test implements InnerInterface{ 26 //这里不用写任何方法,也不报错 27 28 public static void main(String[]args){ 29 Test t = new Test(); 30 t.f2(); //这里t访问不到f1方法 31 } 32 @Override 33 public void f2() { 34 System.out.println("f2"); 35 } 36 }
结果如下:

这里实现InnerInterface ,只需要实现该接口本身的方法就可以,不需要实现接口中定义的接口的方法。关于接口中定义接口,目前认为只是为了完善语法,但是没什么地方用到。
六、接口和工厂
1 public interface Service { 2 void f1(); 3 void f2(); 4 } 5 6 7 public interface ServiceFactory { 8 Service getService(); 9 } 10 11 12 /** 13 * Service 的实现 14 */ 15 public class ImplementsService1 implements Service{ 16 @Override 17 public void f1() { 18 System.out.println("实现f1"); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void f2() { 23 System.out.println("实现f2"); 24 } 25 } 26 27 28 29 public class ImplementsService2 implements Service{ 30 @Override 31 public void f1() { 32 System.out.println("----实现f1"); 33 } 34 35 @Override 36 public void f2() { 37 System.out.println("----实现f2"); 38 } 39 } 40 41 42 class FactoryImpl1 implements ServiceFactory{ 43 @Override 44 public Service getService() { 45 return new ImplementsService1(); 46 } 47 } 48 49 class FactoryImpl2 implements ServiceFactory{ 50 @Override 51 public Service getService() { 52 return new ImplementsService2(); 53 } 54 } 55 56 57 public class Test{ 58 public static void serviceConsumer(ServiceFactory factory) { 59 Service s = factory.getService(); 60 s.f1(); 61 s.f2(); 62 } 63 64 public static void main(String[]args){ 65 Test.serviceConsumer(new FactoryImpl1()); 66 Test.serviceConsumer(new FactoryImpl2()); 67 } 68 }
结果如下:

这里,对于服务,设定了接口Service, 对于工厂也设定接口 ServiceFacotry ,然后当想要调用某种服务的时候,就创建能提供这种服务的工厂。关于工厂模式的详解,在六(3)博客中介绍。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kaiguoguo/p/4681519.html