标签:style blog class code color width
1,数组
对数组只能进行两种操作,1确定数组的大小,2获得数组第一个元素的指针,其他的操作均是通过指针来实现的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 |
#include <stdio.h>main(){ int
a[2][3]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}}; int
*p,(*q)[3]; p=a[2]; q=a;} |
int a[2][3]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
a为一个数组(A),数组的维度为3,元素为数组(B),数组(B)的维度为4 元素为int 类型
a[2]为数组(A)的一个元素,为数组(B)的首地址
p=a[2]; 为p指向a[2]的第一个元素的地址,第一个元素为 int 类型,p为指向int 类型的指针,故是相符的
p=a,是不正确的,a为指向数组(B)的指针
q为指向数组(B)的指针,故q=a是正确的。
下标引用和指针之间的关系?
|
1
2
3 |
i=a[2][3];i=*(a[2]+3);i=*(*(a+2)+3); |
根据指针的而不同,吃处+3,地址可能是不同的
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 |
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>main(){char
*p ,*q;int
*a;p=malloc(sizeof(char));a=malloc(sizeof(int));printf("%d \n",p);printf("%d\n",p+1);printf("%d \n",a);printf("%d \n",a+1);} |
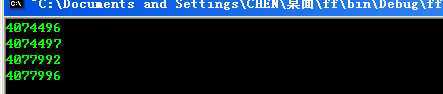
p为指向char 的指针,p+1的地址是+1
q为指向int 的指针,q+1的地址是+4
2 指针
空指针并非空字符串
标签:style blog class code color width
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/chen-/p/3705788.html