标签:
|
何首乌 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||||||||||||
| 科学分类 | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| 二名法 | ||||||||||||||
| Fallopia multiflora (Thunb.) Haraldson |
何首乌(学名:Fallopia multiflora 或者Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.),又名野苗、交藤、交茎、夜合[1]、地精、桃柳藤[2]、赤葛、九真藤[3]、芮草、蛇草[4]、陈知白[5]、马肝石、九真藤、疮帚[6]等。为蓼科植物,有雌雄二种(赤,白二种)[7],性喜高温高湿,生长于海拔1000米以上的山麓。
何首乌状如人形[8],可促进毛发生长的功效,故称何首乌。《开宝本草》称何首乌“黑须发,悦颜色,久服长筋骨,益精髓,延年不老”。中国古代“四仙药”(何首乌、黄精、地黄与灵芝)之一[9]。
主产于中国大陆的河南、湖北、贵州、四川、江苏、广西等地,日本亦有。
多年生缠绕性草本植物;具有粗壮块状根茎;卵状心形叶子,全缘,两面粗糙无毛,鞘筒状托叶,无缘毛,常破裂而早落;秋季开黄白色花,圆锥花序,花被外方三片果期增大,肥厚,背部具鞘,包于瘦果外面。
何首乌据称是元和七年(813年)顺州南河县(今广西陆川县西)人何田儿所发现,常年服用活到160岁[10]。反对者则援引《全唐文》所录的中唐李翱的《何首乌录》,何首乌是发现者孙子的姓名,所谓黑发功效乃“望文生义”引发的讹传。[11]
现代医学证实何首乌内含酚类化合物,根部含蒽醌类成分大黄酚、大黄素、大黄酸,此外,含淀粉45.2%、粗脂肪3.1%、卵磷脂3.7%等。《本草纲目》记载,“此物气温,味苦涩。苦补肾,温补肝,涩能收敛精气。所以能养血益肝,固精益肾,健筋骨,乌髭髪,为滋补良药,不寒不燥,功在地黄、天门冬诸药之上。”可治肝肾阴亏,发须早白。名方“首乌延寿丸”、“七宝美髯丸”就是以首乌为主药制成[来源请求]。
近来,有报导其单体或制剂有肝毒性,主要表现为急慢性肝炎、黄疸等[12]。有研究认为[13],其活性成分二苯乙烯苷很可能具有保肝护肝及导致肝炎的双重作用;然而,另一研究[14]却认为,其肝毒性主要是由蒽醌类化合物所致,与二苯乙烯苷无关。2013年,国家食品药品监督管理总局已将部分含何首乌草本的非处方类药物列为处方类药物.
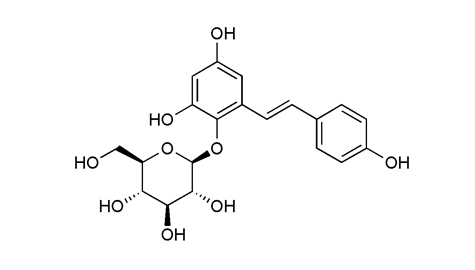 |
|
| 植物來源 | 何首烏Polygonum multiflorum Thunb[1] | |||||||||||
| 異名 | 2,3,5,4‘-四-羥基茋-2-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷, 2,3,5,4‘–四羥基對苯乙烯-2-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷, 2,3,5,4-四羥基二苯乙烯-2-o-葡萄糖苷, 2,3,5,4‘-四羥基二苯乙烯-2-O-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖, 四羥基茋葡萄糖苷 | |||||||||||
| 生物活性 | 2,3,5,4‘-四羥基茋-2-o-β-d-葡萄糖苷作用于多巴胺能神經元[2] [3] [4], 6-OHDA-誘導的PC12細胞雕亡[5]及預防骨質疏鬆[6]。抗氧化及清除自由基[7], 抗動脈粥樣硬化[8] [9], 且體內體外均有對於抗缺血性腦損傷明顯的神經保護作用[10], 2,3,5,4‘-四羥基茋-2-o-β-d-葡萄糖苷可抑制基因轉染PC12細胞的α-Syn的過度表達及聚集[11]及血小板引發的生長因子BB誘導的血管平滑肌細胞增殖[12]。減少人臍動脈內皮細胞的雕亡[13], 抗阿爾茨海默氏症[14], 及降低血管內皮功能障礙作用[15]。 | |||||||||||
| 鑑定 |
|
|||||||||||
| 分析方法 | TLC[16] |
|
||||||||||
| HPLC[17] |
|
|||||||||||
| HPLC[1] |
|
|||||||||||
| LC-MS[18] |
|
|||||||||||
| 樣品製備 | 方法一 |
|
||||||||||
| 參考文獻 | [1] | Yao, S., et al. (2006). "Preparative isolation and purification of chemical constituents from the root of Polygonum multiflorum by high-speed counter-current chromatography." J Chromatogr A 1115(1-2): 64-71. | ||||||||||
| [2] | Zhang, L., et al. (2012). "Effect of TSG on nigral dopaminergic transporter (DAT) in MPTP mouse model of Parkinson‘s disease." Shenjing Jiepouxue Zazhi 28(1): 33-37. | |||||||||||
| [3] | Sun, F.-l., et al. (2011). "Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against MPP+-induced cytotoxicity." Eur. J. Pharmacol. 660(2-3): 283-290. | |||||||||||
| [4] | Qin, R., et al. (2011). "Protection by tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside against neurotoxicity induced by MPP+: The involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway activation." Toxicol. Lett. 202(1): 1-7. | |||||||||||
| [5] | Tao, L., et al. (2011). "TSG attenuated 6-OHDA-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by the inhibition of ROS." Shenjing Jiepouxue Zazhi 27(1): 19-23. | |||||||||||
| [6] | Zhang, J. K., et al. (2012). "Protective effect of tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside against hydrogen peroxide-induced dysfunction and oxidative stress in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells." Eur J Pharmacol 689(1-3): 31-37. | |||||||||||
| [7] | Zhang, S. H., et al. (2009). "Protective effect of tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside on cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin in vitro and in vivo." Acta Pharmacol Sin 30(11): 1479-1487. | |||||||||||
| [8] | Yao, W., et al. (2013). "Proteomic analysis for anti-atherosclerotic effect of tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside in rats." Biomed. Pharmacother. 67(2): 140-145. | |||||||||||
| [9] | Yao, W., et al. (2013). "Proteomic analysis for anti-atherosclerotic effect of tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside in rats." Biomed Pharmacother 67(2): 140-145. | |||||||||||
| [10] | Wang, X., et al. (2008). "Protective effects of 2,3,5,4‘-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-beta-d-glucoside, an active component of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb, on experimental colitis in mice." Eur J Pharmacol 578(2-3): 339-348. | |||||||||||
| [11] | Liu, Y., et al. (2012). "Effects of tetrahydroxy-stilbene glycoside on α-synuclein overexpression and ubiquitin-proteasome system in gene-transfected PC12 cells." Zhongguo Yaoxue Zazhi (Beijing, China) 47(1): 34-39. | |||||||||||
| [12] | Xu, X.-L., et al. (2012). "2,3,4‘,5-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside Inhibits Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Involvement of NO/cGMP/PKG Pathway." Phytother. Res. 26(7): 1068-1074. | |||||||||||
| [13] | Li, J., et al. (2013). "Effects of tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside on apoptosis and expressions of bcl-2/bax/caspase-3 in HUVECs treated with homocysteine." Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi 29(4): 743-747. | |||||||||||
| [14] | Zhou, L., et al. (2012). "Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside improves the learning and memory of amyloid-β1-42-injected rats and may be connected to synaptic changes in the hippocampus." Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 90(11): 1446-1455. | |||||||||||
| [15] | Zhang, W., et al. (2009). "Effects of 2,3,4‘,5-tetrahydroxystilbene 2-O-β-D-glucoside on vascular endothelial dysfunction in atherogenic-diet rats." Planta Med. 75(11): 1209-1214. | |||||||||||
| [16] | Hu, Y., et al. (2009). "Quality standard for YiShenyangyuan mixture." Guangdong Yaoxueyuan Xuebao 25(2): 157-159. | |||||||||||
| [17] | Xie, D., et al. (2003). "Determination of 2,3,5,4‘-tetrahydroxystibene-2-O-β-D-glucoside in Yangxue Bushen oral liquid by HPLC." Guangdong Yaoxueyuan Xuebao 19(4): 332-333, 339. | |||||||||||
| [18] | Zhao, Y.-Y., et al. (2013). "Pharmacokinetics of 2,3,5,4‘-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside in rat using ultra-performance LC-quadrupole TOF-MS." J. Sep. Sci. 36(5): 863-871. | |||||||||||
| 連結 |  中藥材圖像數據庫 中藥材圖像數據庫  藥用植物圖像數據庫 藥用植物圖像數據庫 |
|||||||||||
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/biopy/p/4690475.html