In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm describes a set of procedures or instructions that define a procedure. The term has become increasing popular since the advent of cheap and reliable computers. Many companies now
employ a single coder to write an algorithm that will replace many other employees. An added benefit to the employer is that the coder will also become redundant once their work is done.
1
You are now the signle coder, and have been assigned a new task writing code, since your boss would like to replace many other employees (and you when you become redundant once your task is complete).
Your code should be able to complete a task to replace these employees who do nothing all day but eating: make the digest sum.
By saying “digest sum” we study some properties of data. For the sake of simplicity, our data is a set of integers. Your code should give response to following operations:
1. add x – add the element x to the set;
2. del x – remove the element x from the set;
3. sum – find the digest sum of the set. The digest sum should be understood by
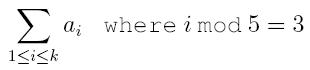
where the set S is written as {a
1, a
2, ... , a
k} satisfying a
1 < a
2 < a
3 < ... < a
k
Can you complete this task (and be then fired)?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 See http://uncyclopedia.wikia.com/wiki/Algorithm
There’re several test cases.
In each test case, the first line contains one integer N ( 1 <= N <= 105 ), the number of operations to process.
Then following is n lines, each one containing one of three operations: “add x” or “del x” or “sum”.
You may assume that 1 <= x <= 109.
Please see the sample for detailed format.
For any “add x” it is guaranteed that x is not currently in the set just before this operation.
For any “del x” it is guaranteed that x must currently be in the set just before this operation.
Please process until EOF (End Of File).
For each operation “sum” please print one line containing exactly one integer denoting the digest sum of the current set. Print 0 if the set is empty.
9
add 1
add 2
add 3
add 4
add 5
sum
add 6
del 3
sum
6
add 1
add 3
add 5
add 7
add 9
sum
3
4
5
Hint
C++ maybe run faster than G++ in this problem.
这个题目纠结好长时间了,线段树版本网上题解也不是很详细,可能怪我自己看不懂…… 。 暴力vector 步步模拟一样能过,得过且过吧,
以后线段树水平加深之后再回头写个线段树版本 希望
~ 第一次学着用vim调试代码。感觉还行吧~ 只是好多好多用法现在还都没有
掌握,vi的强大施展不开吧~! 、
是不是想当眩的vimrc的配置? 想个性化定制可以联系我。
 好了 ac代码水过:
好了 ac代码水过:
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string.h>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
vector<int>cnt;
int n;
int main(){
char op[5];
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++){
scanf("%s",op);
if(op[0] == 'a'){
int x;scanf("%d",&x);
cnt.insert(lower_bound(cnt.begin(),cnt.end(), x), x);
}
else if(op[0] == 'd'){
int x;scanf("%d",&x);
cnt.erase(lower_bound(cnt.begin(),cnt.end(),x));
}
else {
long long ans = 0;
for(int i = 2; i < cnt.size(); i+=5){
ans += cnt[i];
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}
cnt.clear();
}
return 0;
}
好了 ac代码水过: