标签:
元素的位置是以像素来度量的,向右代表X坐标的增加,向下代表Y坐标的增加。但是,有两个不同的点作为坐标系的原点:元素的X和Y坐标可以相对于文档的左上角或者相对于其中显示文档的视口的左上角。在顶级窗口和标签页中,“视口”只是实际显示文档内容的浏览器的一部分:它不包括浏览器“外壳”(如菜单,工具条件和标签页)。当讨论元素的位置时,必须弄清楚所使用的坐标时文档坐标还是视口坐标。【注】视口坐标有时也叫窗口坐标。
举例说明:在文档坐标中如果一个元素的Y坐标时200px,并且用户已经把浏览器向下滑动75px,那么视口坐标中元素的Y坐标时125px。同理,在视口坐标中如果一个元素的X坐标是400px,并且用户已经水平滚动了视口200px,那么文档坐标中元素的X坐标是600px。
浏览器兼容:IE 9或IE9+、Goggle、FireFox
console.log(window.innerWidth);
console.log(window.innerHeight);
浏览器兼容:IE 9或IE9+、Goggle、FireFox
console.log(window.outerWidth);
console.log(window.outerHeight);
浏览器兼容:IE 9或IE9+、Goggle、FireFox
console.log(window.pageXOffset); console.log(window.pageYOffset); /*主流浏览器都支持该属性,IE 8+,建议用上述来获取滚动条偏移*/ console.log(window.document.documentElement.scrollLeft); console.log(window.document.documentElement.scrollTop); /*IE8之前或更早的版本用此*/ console.log(window.document.body.scrollLeft); console.log(window.document.body.scrollTop); /*对怪异模式下的浏览器*/
如图所示:
console.log(window.scrollX); console.log(window.scrollY); /*在IE 6+都不怎么支持此属性,所以不再建议使用*/
浏览器兼容:IE 6以及IE 6+、Goggle、FireFox
console.log(screen.width);
console.log(screen.height);
浏览器兼容:IE 6以及IE 6+、Goggle、FireFox
console.log(screen.availHeight);
console.log(screen.availWidth);
为了理解充分理解元素中的client-、scroll-、offset-属性利用一张图即可!
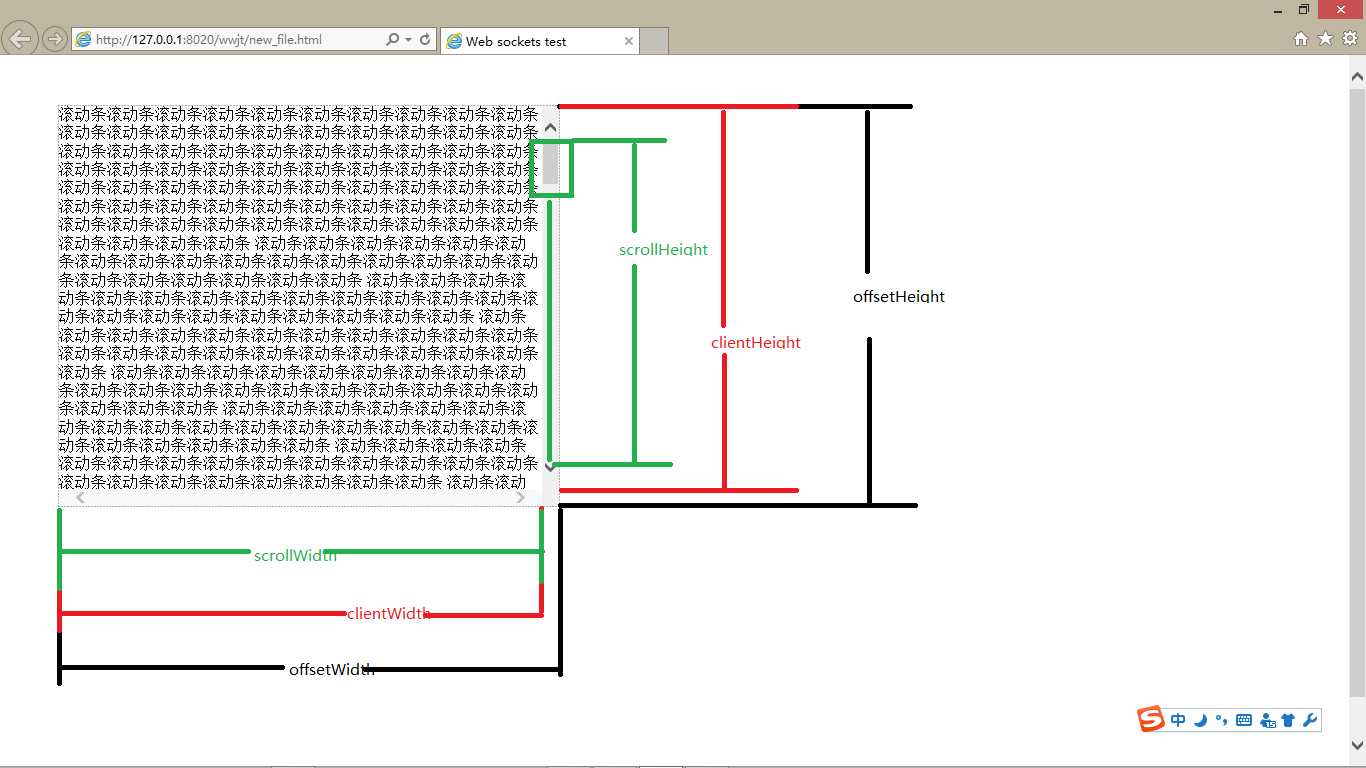
1 function getElementPostion(e) { 2 var x = 0, 3 y = 0; 4 while (e != null) { 5 x += e.offsetLeft; 6 y += e.offsetTop; 7 e = e.offsetParent; 8 } 9 return { 10 x: x, 11 y: y 12 }; 13 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/CreateMyself/p/4714641.html