关于SIFT的原理已经有很多大牛的博客上做了解析,本文重点将以Rob Hess等人用C实现的代码做解析,结合代码SIFT原理会更容易理解。一些难理解点的用了☆标注。
欢迎大家批评指正!
SIFT(Scale-invariant feature transform)即尺度不变特征转换,提取的局部特征点具有尺度不变性,且对于旋转,亮度,噪声等有很高的稳定性。
1.图像预处理
2.构建高斯金字塔(不同尺度下的图像)
3.生成DOG尺度空间
4.关键点搜索与定位
5.计算特征点对应原图的位置
6.为特征点分配方向角
7.构建特征描述子
/**
Finds SIFT features in an image using user-specified parameter values. All
detected features are stored in the array pointed to by \a feat.
*/
int _sift_features( IplImage* img, struct feature** feat, int intvls,
double sigma, double contr_thr, int curv_thr,
int img_dbl, int descr_width, int descr_hist_bins )
{
IplImage* init_img;
IplImage*** gauss_pyr, *** dog_pyr;
CvMemStorage* storage;
CvSeq* features;
int octvs, i, n = 0;
/* check arguments */
if( ! img )
fatal_error( "NULL pointer error, %s, line %d", __FILE__, __LINE__ );
if( ! feat )
fatal_error( "NULL pointer error, %s, line %d", __FILE__, __LINE__ );
/* build scale space pyramid; smallest dimension of top level is ~4 pixels */
init_img = create_init_img( img, img_dbl, sigma ); //对进行图片预处理
octvs = log( MIN( init_img->width, init_img->height ) ) / log(2) - 2; //计算高斯金字塔的组数(octave),同时保证顶层至少有4个像素点
gauss_pyr = build_gauss_pyr( init_img, octvs, intvls, sigma ); //建立高斯金字塔
dog_pyr = build_dog_pyr( gauss_pyr, octvs, intvls ); //DOG尺度空间
storage = cvCreateMemStorage( 0 );
features = scale_space_extrema( dog_pyr, octvs, intvls, contr_thr, //极值点检测,并去除不稳定特征点
curv_thr, storage );
calc_feature_scales( features, sigma, intvls ); //计算特征点所在的尺度
if( img_dbl )
adjust_for_img_dbl( features ); //如果图像初始被扩大了2倍,所有坐标与尺度要除以2
calc_feature_oris( features, gauss_pyr ); //计算特征点的方向角
compute_descriptors( features, gauss_pyr, descr_width, descr_hist_bins );//计算特征描述子
/* sort features by decreasing scale and move from CvSeq to array */
cvSeqSort( features, (CvCmpFunc)feature_cmp, NULL ); //对特征点按尺度排序
n = features->total;
*feat = calloc( n, sizeof(struct feature) );
*feat = cvCvtSeqToArray( features, *feat, CV_WHOLE_SEQ );
for( i = 0; i < n; i++ )
{
free( (*feat)[i].feature_data );
(*feat)[i].feature_data = NULL;
}
cvReleaseMemStorage( &storage );
cvReleaseImage( &init_img );
release_pyr( &gauss_pyr, octvs, intvls + 3 );
release_pyr( &dog_pyr, octvs, intvls + 2 );
return n;
}
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————
/************************ Functions prototyped here **************************/
/*
Converts an image to 8-bit grayscale and Gaussian-smooths it. The image is
optionally doubled in size prior to smoothing.
@param img input image
@param img_dbl if true, image is doubled in size prior to smoothing
@param sigma total std of Gaussian smoothing
*/
static IplImage* create_init_img( IplImage* img, int img_dbl, double sigma )
{
IplImage* gray, * dbl;
double sig_diff;
gray = convert_to_gray32( img ); //转换为32位灰度图
if( img_dbl ) // 图像被放大二倍
{
sig_diff = sqrt( sigma * sigma - SIFT_INIT_SIGMA * SIFT_INIT_SIGMA * 4 ); // sigma = 1.6 , SIFT_INIT_SIGMA = 0.5 lowe认为图像在尺度0.5下最清晰
dbl = cvCreateImage( cvSize( img->width*2, img->height*2 ),
IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1 );
cvResize( gray, dbl, CV_INTER_CUBIC ); //双三次插值方法 放大图像
cvSmooth( dbl, dbl, CV_GAUSSIAN, 0, 0, sig_diff, sig_diff ); //高斯平滑
cvReleaseImage( &gray );
return dbl;
}
else
{
sig_diff = sqrt( sigma * sigma - SIFT_INIT_SIGMA * SIFT_INIT_SIGMA );
cvSmooth( gray, gray, CV_GAUSSIAN, 0, 0, sig_diff, sig_diff ); // 高斯平滑
return gray;
}
}
 。
。


 平滑图像,效果是一样的。
平滑图像,效果是一样的。/*
Builds Gaussian scale space pyramid from an image
@param base base image of the pyramid
@param octvs number of octaves of scale space
@param intvls number of intervals per octave
@param sigma amount of Gaussian smoothing per octave
@return Returns a Gaussian scale space pyramid as an octvs x (intvls + 3)
array
给定组数(octave)和层数(intvls),以及初始平滑系数sigma,构建高斯金字塔
返回的每组中层数为intvls+3
*/
static IplImage*** build_gauss_pyr( IplImage* base, int octvs,
int intvls, double sigma )
{
IplImage*** gauss_pyr;
const int _intvls = intvls; // lowe 采用了每组层数(intvls)为 3
// double sig_total, sig_prev;
double k;
int i, o;
double *sig = (double *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(_intvls+3)); //存储每组的高斯平滑因子,每组对应的平滑因子都相同
gauss_pyr = calloc( octvs, sizeof( IplImage** ) );
for( i = 0; i < octvs; i++ )
gauss_pyr[i] = calloc( intvls + 3, sizeof( IplImage *) );
/*
precompute Gaussian sigmas using the following formula:
\sigma_{total}^2 = \sigma_{i}^2 + \sigma_{i-1}^2
sig[i] is the incremental sigma value needed to compute
the actual sigma of level i. Keeping track of incremental
sigmas vs. total sigmas keeps the gaussian kernel small.
*/
k = pow( 2.0, 1.0 / intvls ); // k = 2^(1/S)
sig[0] = sigma;
sig[1] = sigma * sqrt( k*k- 1 );
for (i = 2; i < intvls + 3; i++)
sig[i] = sig[i-1] * k; //每组对应的平滑因子为 σ , sqrt(k^2 -1)* σ, sqrt(k^2 -1)* kσ , ...
for( o = 0; o < octvs; o++ )
for( i = 0; i < intvls + 3; i++ )
{
if( o == 0 && i == 0 )
gauss_pyr[o][i] = cvCloneImage(base); //第一组,第一层为原图
/* base of new octvave is halved image from end of previous octave */
else if( i == 0 )
gauss_pyr[o][i] = downsample( gauss_pyr[o-1][intvls] ); //第一层图像由上一层倒数第三张隔点采样得到
/* blur the current octave's last image to create the next one */
else
{
gauss_pyr[o][i] = cvCreateImage( cvGetSize(gauss_pyr[o][i-1]),
IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1 );
cvSmooth( gauss_pyr[o][i-1], gauss_pyr[o][i],
CV_GAUSSIAN, 0, 0, sig[i], sig[i] ); //高斯平滑
}
}
return gauss_pyr;
}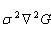 非常近似,且
非常近似,且





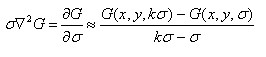



static IplImage*** build_dog_pyr( IplImage*** gauss_pyr, int octvs, int intvls )
{
IplImage*** dog_pyr;
int i, o;
dog_pyr = calloc( octvs, sizeof( IplImage** ) );
for( i = 0; i < octvs; i++ )
dog_pyr[i] = calloc( intvls + 2, sizeof(IplImage*) );
for( o = 0; o < octvs; o++ )
for( i = 0; i < intvls + 2; i++ )
{
dog_pyr[o][i] = cvCreateImage( cvGetSize(gauss_pyr[o][i]),
IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1 );
cvSub( gauss_pyr[o][i+1], gauss_pyr[o][i], dog_pyr[o][i], NULL ); //相邻两层图像相减,结果放在dog_pyr数组内
}
return dog_pyr;
}
/*
Detects features at extrema in DoG scale space. Bad features are discarded
based on contrast and ratio of principal curvatures.
@return Returns an array of detected features whose scales, orientations,
and descriptors are yet to be determined.
*/
static CvSeq* scale_space_extrema( IplImage*** dog_pyr, int octvs, int intvls,
double contr_thr, int curv_thr,
CvMemStorage* storage )
{
CvSeq* features;
double prelim_contr_thr = 0.5 * contr_thr / intvls; //极值比较前的阈值处理
struct feature* feat;
struct detection_data* ddata;
int o, i, r, c;
features = cvCreateSeq( 0, sizeof(CvSeq), sizeof(struct feature), storage );
for( o = 0; o < octvs; o++ ) //对DOG尺度空间上,遍历从第二层图像开始到倒数第二层图像上,每个像素点
for( i = 1; i <= intvls; i++ )
for(r = SIFT_IMG_BORDER; r < dog_pyr[o][0]->height-SIFT_IMG_BORDER; r++)
for(c = SIFT_IMG_BORDER; c < dog_pyr[o][0]->width-SIFT_IMG_BORDER; c++)
/* perform preliminary check on contrast */
if( ABS( pixval32f( dog_pyr[o][i], r, c ) ) > prelim_contr_thr ) // 排除像素值小于阈值prelim_contr_thr的点,提高稳定性
if( is_extremum( dog_pyr, o, i, r, c ) ) //与周围26个像素值比较,是否极大值或者极小值点
{
feat = interp_extremum(dog_pyr, o, i, r, c, intvls, contr_thr); //插值处理,找到准确的特征点坐标
if( feat )
{
ddata = feat_detection_data( feat );
if( ! is_too_edge_like( dog_pyr[ddata->octv][ddata->intvl], //根据Hessian矩阵 判断是否为边缘上的点
ddata->r, ddata->c, curv_thr ) )
{
cvSeqPush( features, feat ); //是特征点进入特征点序列
}
else
free( ddata );
free( feat );
}
}
return features;
}
/*
Determines whether a pixel is a scale-space extremum by comparing it to it's
3x3x3 pixel neighborhood.
*/
static int is_extremum( IplImage*** dog_pyr, int octv, int intvl, int r, int c )
{
double val = pixval32f( dog_pyr[octv][intvl], r, c );
int i, j, k;
/* check for maximum */
if( val > 0 )
{
for( i = -1; i <= 1; i++ )
for( j = -1; j <= 1; j++ )
for( k = -1; k <= 1; k++ )
if( val < pixval32f( dog_pyr[octv][intvl+i], r + j, c + k ) )
return 0;
}
/* check for minimum */
else
{
for( i = -1; i <= 1; i++ )
for( j = -1; j <= 1; j++ )
for( k = -1; k <= 1; k++ )
if( val > pixval32f( dog_pyr[octv][intvl+i], r + j, c + k ) )
return 0;
}
return 1;
} ,其中
,其中


 是一个三维矢量,矢量在任何一个方向上的偏移量大于0.5时,意味着已经偏离了原像素点,这样的特征坐标位置需要更新或者继续插值计算。算法实现过程中,为了保证插值能够收敛,设置了最大插值次数(lowe 设置了5次)。同时当
是一个三维矢量,矢量在任何一个方向上的偏移量大于0.5时,意味着已经偏离了原像素点,这样的特征坐标位置需要更新或者继续插值计算。算法实现过程中,为了保证插值能够收敛,设置了最大插值次数(lowe 设置了5次)。同时当 时(本文阈值采用了0.04/S)
,特征点才被保留,因为响应值过小的点,容易受噪声的干扰而不稳定。
时(本文阈值采用了0.04/S)
,特征点才被保留,因为响应值过小的点,容易受噪声的干扰而不稳定。/*
Performs one step of extremum interpolation. Based on Eqn. (3) in Lowe's
paper.
r,c 为特征点位置,xi,xr,xc,保存三个方向的偏移量
*/
static void interp_step( IplImage*** dog_pyr, int octv, int intvl, int r, int c,
double* xi, double* xr, double* xc )
{
CvMat* dD, * H, * H_inv, X;
double x[3] = { 0 };
dD = deriv_3D( dog_pyr, octv, intvl, r, c ); //计算三个方向的梯度
H = hessian_3D( dog_pyr, octv, intvl, r, c ); // 计算3维空间的hessian矩阵
H_inv = cvCreateMat( 3, 3, CV_64FC1 );
cvInvert( H, H_inv, CV_SVD ); //计算逆矩阵
cvInitMatHeader( &X, 3, 1, CV_64FC1, x, CV_AUTOSTEP );
cvGEMM( H_inv, dD, -1, NULL, 0, &X, 0 ); //广义乘法
cvReleaseMat( &dD );
cvReleaseMat( &H );
cvReleaseMat( &H_inv );
*xi = x[2];
*xr = x[1];
*xc = x[0];
}/*
Interpolates a scale-space extremum's location and scale to subpixel
accuracy to form an image feature.
*/
static struct feature* interp_extremum( IplImage*** dog_pyr, int octv, //通过拟合求取准确的特征点位置
int intvl, int r, int c, int intvls,
double contr_thr )
{
struct feature* feat;
struct detection_data* ddata;
double xi, xr, xc, contr;
int i = 0;
while( i < SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS ) //在最大迭代次数范围内进行
{
interp_step( dog_pyr, octv, intvl, r, c, &xi, &xr, &xc ); //插值后得到的三个方向的偏移量(xi,xr,xc)
if( ABS( xi ) < 0.5 && ABS( xr ) < 0.5 && ABS( xc ) < 0.5 )
break;
c += cvRound( xc ); //更新位置
r += cvRound( xr );
intvl += cvRound( xi );
if( intvl < 1 ||
intvl > intvls ||
c < SIFT_IMG_BORDER ||
r < SIFT_IMG_BORDER ||
c >= dog_pyr[octv][0]->width - SIFT_IMG_BORDER ||
r >= dog_pyr[octv][0]->height - SIFT_IMG_BORDER )
{
return NULL;
}
i++;
}
/* ensure convergence of interpolation */
if( i >= SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS )
return NULL;
contr = interp_contr( dog_pyr, octv, intvl, r, c, xi, xr, xc ); //计算插值后对应的函数值
if( ABS( contr ) < contr_thr / intvls ) //小于阈值(0.04/S)的点,则丢弃
return NULL;
feat = new_feature();
ddata = feat_detection_data( feat );
feat->img_pt.x = feat->x = ( c + xc ) * pow( 2.0, octv ); // 计算特征点根据降采样的次数对应于原图中位置
feat->img_pt.y = feat->y = ( r + xr ) * pow( 2.0, octv );
ddata->r = r; // 在本尺度内的坐标位置
ddata->c = c;
ddata->octv = octv; //组信息
ddata->intvl = intvl; // 层信息
ddata->subintvl = xi; // 层方向的偏移量
return feat;
}
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/47377611