标签:
题目:
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Note: next() and hasNext() should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.
思路:
想实现二叉搜索树的Iterator,每次找当前的最小值。画个图就知道,这个题目就是考察二叉树的中序遍历而已。
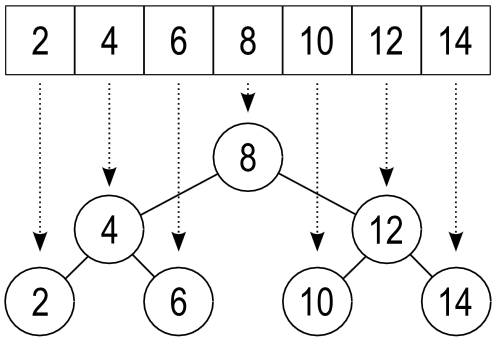
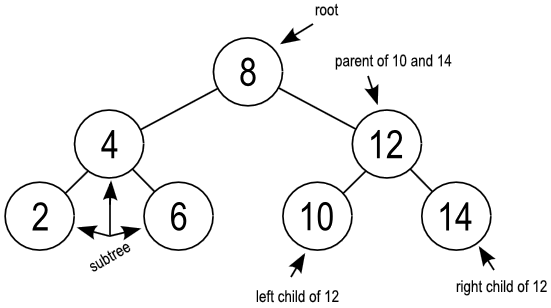
再不考虑空间复杂度的情况下,我们可以很简单的写出二叉搜索树的AC代码:
1 import java.util.ArrayDeque; 2 import java.util.Stack; 3 4 5 public class BSTIterator { 6 private ArrayDeque<TreeNode> mArrayDeque; 7 8 public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) { 9 mArrayDeque = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>(); 10 bTreeInorderTraverse(root); 11 } 12 13 private void bTreeInorderTraverse(TreeNode root) { 14 TreeNode p = root; 15 Stack<TreeNode> tmpStack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); 16 17 while (p != null || ! tmpStack.empty()) { 18 if (p != null) { 19 tmpStack.push(p); 20 p = p.left; 21 } else { 22 p = tmpStack.pop(); 23 mArrayDeque.add(p); 24 p = p.right; 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 29 public boolean hasNext() { 30 return ! mArrayDeque.isEmpty(); 31 } 32 33 public int next() { 34 if (hasNext()) { 35 return mArrayDeque.poll().val; 36 } else { 37 return -1; 38 } 39 } 40 41 public static class TreeNode { 42 int val; 43 TreeNode left; 44 TreeNode right; 45 TreeNode(int x) { 46 val = x; 47 } 48 } 49 }
1 public class BSTIterator { 2 3 public LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); 4 public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) 5 { 6 while(root!=null) 7 { 8 stack.push(root); 9 root=root.left; 10 } 11 12 } 13 14 public boolean hasNext() 15 { 16 return !stack.isEmpty(); 17 } 18 19 public int next() 20 { 21 TreeNode p=stack.pop(); 22 int result=p.val; 23 if(p.right!=null) 24 { 25 TreeNode node = p.right; 26 while(node != null) 27 { 28 stack.push(node); 29 node=node.left; 30 } 31 } 32 return result; 33 } 34 35 }
reference: http://ju.outofmemory.cn/entry/115846
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hygeia/p/4716926.html