投影是指将对象转换为一种新形式的操作,该形式通常只包含那些将随后使用的属性。 通过使用投影,您可以构建依据每个对象生成的新类型。 您可以映射属性,并对该属性执行数学函数。 还可以在不更改原始对象的情况下映射该对象。
下面一节中列出了执行投影的标准查询运算符方法。
 Select
Select
下面的示例使用 C# 中的 select 子句或 Visual Basic 中的 Select 子句来映射字符串列表中每个字符串的第一个字母。
 SelectMany
SelectMany
下面的示例使用多个 from 子句(在 C# 中)或 From 子句(在 Visual Basic 中)来映射字符串列表中每个字符串中的每个单词。
List<string> phrases = new List<string>() { "an apple a day", "the quick brown fox" };
var query = from phrase in phrases
from word in phrase.Split(‘ ‘)
select word;
foreach (string s in query)
Console.WriteLine(s);
/* This code produces the following output:
an
apple
a
day
the
quick
brown
fox
*/
Select() 和 SelectMany() 的工作都是依据源值生成一个或多个结果值。 Select() 为每个源值生成一个结果值。 因此,总体结果是一个与源集合具有相同元素数目的集合。 与之相反,SelectMany() 将生成单一总体结果,其中包含来自每个源值的串联子集合。 作为参数传递到 SelectMany() 的转换函数必须为每个源值返回一个可枚举值序列。 然后,SelectMany() 将串联这些可枚举序列以创建一个大的序列。
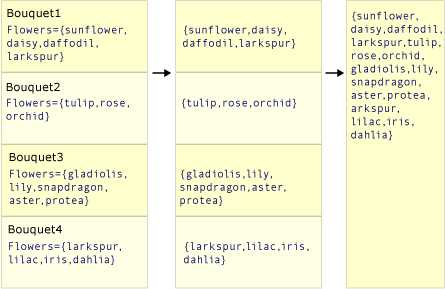
下面两个插图演示了这两个方法的操作之间的概念性区别。 在每种情况下,假定选择器(转换)函数从每个源值中选择一个由花卉数据组成的数组。
下图描述 Select() 如何返回一个与源集合具有相同元素数目的集合。

下图描述 SelectMany() 如何将中间数组序列串联为一个最终结果值,其中包含每个中间数组中的每个值。
 代码示例
代码示例
下面的示例比较 Select() 和 SelectMany() 的行为。 代码将通过从源集合的每个花卉名称列表中提取前两项来创建一个“花束”。 在此示例中,转换函数Select<TSource, TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TSource, TResult>) 使用的“单一值”本身就是一个值集合。 这需要额外的 foreach(Visual Basic 中为 For Each)循环,以便枚举每个子序列中的每个字符串。
class Bouquet
{
public List<string> Flowers { get; set; }
}
static void SelectVsSelectMany()
{
List<Bouquet> bouquets = new List<Bouquet>() {
new Bouquet { Flowers = new List<string> { "sunflower", "daisy", "daffodil", "larkspur" }},
new Bouquet{ Flowers = new List<string> { "tulip", "rose", "orchid" }},
new Bouquet{ Flowers = new List<string> { "gladiolis", "lily", "snapdragon", "aster", "protea" }},
new Bouquet{ Flowers = new List<string> { "larkspur", "lilac", "iris", "dahlia" }}
};
// *********** Select ***********
IEnumerable<List<string>> query1 = bouquets.Select(bq => bq.Flowers);
// ********* SelectMany *********
IEnumerable<string> query2 = bouquets.SelectMany(bq => bq.Flowers);
Console.WriteLine("Results by using Select():");
// Note the extra foreach loop here.
foreach (IEnumerable<String> collection in query1)
foreach (string item in collection)
Console.WriteLine(item);
Console.WriteLine("\nResults by using SelectMany():");
foreach (string item in query2)
Console.WriteLine(item);
/* This code produces the following output:
Results by using Select():
sunflower
daisy
daffodil
larkspur
tulip
rose
orchid
gladiolis
lily
snapdragon
aster
protea
larkspur
lilac
iris
dahlia
Results by using SelectMany():
sunflower
daisy
daffodil
larkspur
tulip
rose
orchid
gladiolis
lily
snapdragon
aster
protea
larkspur
lilac
iris
dahlia
*/
}
