标签:
单词:
lipid[‘l?p?d]脂质
N any of a large group of organic compounds that are esters of fatty acids (simple lipids, such as fats and waxes) or closely related substances (compound lipids, such as phospholipids): usually insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol and other organic solvents. They are important structural materials in living organisms 脂质 (Former name lipoid)
fat 脂肪
Fat is a substance contained in foods such as meat, cheese, and butter which forms an energy store in your body.
phospholipid/?f?sf??l?p?d/磷脂
composed of fatty acids, phosphoric acid, and a nitrogenous base: important constituents of all membranes
sterol固醇[‘st??r?l; ‘ster?l]
cholesterol [k?‘lest?r?l] 胆固醇
Cholesterol is a substance that exists in the fat, tissues, and blood of all animals. Too much cholesterol in a person‘s blood can cause heart disease.
hormone激素,荷尔蒙[‘h??m??n]
A hormone is a chemical, usually occurring naturally in your body, that makes an organ of your body do something.
组成:
主要元素C,H,O, 有些脂质含P,N
不溶于水,溶于脂溶性有机溶剂。
常见种类;
脂肪,磷脂,固醇
作用
1.脂质存在于所有细胞,是组成细胞和生物体的重要有机化合物。
2.脂肪是细胞良好储能物质。当生命活动需要时可以分解利用。
3.保温作用:良好绝热体。
4.缓冲减压,保护内脏器官。
磷脂:
构成细胞膜的重要成分。也是构成多种细胞器膜的重要成分。
广泛存在于人和动物的脑,卵细胞,肝脏,以及大豆的种子。
固醇:
包括胆固醇,性激素和维生素D。
胆固醇:构成细胞膜重要成分。参与血液中的脂质运输。
过多摄入会在血管壁上沉积,堵塞血管,危机生命。
性激素:促进人和动物生殖器官的发育,以及生殖细胞的形成。
维生素D:促进人和动物肠道对钙和磷的吸收。
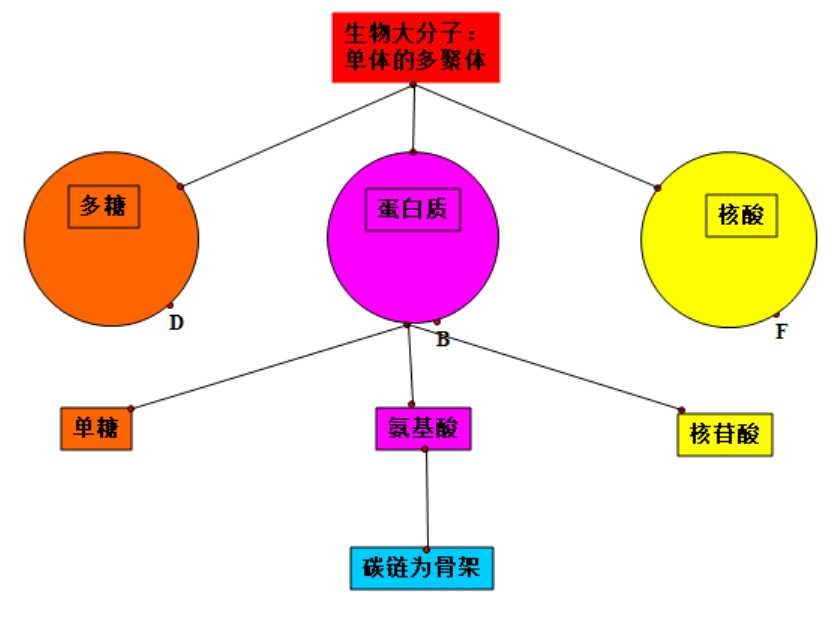
生物大分子以碳链为骨架。
生物大分子是单体的多聚体。
为什么等量的脂肪比糖类含能量多,却不是生物体利用的主要能源物质?
在人体内物质利用顺序是这样的:糖类 脂肪 蛋白质
1.因为糖类转化快 能更快的被人体利用
2.部分细胞只能代谢糖类而不能代谢脂肪(脑神经细胞只能利用糖类分解来获得能量)
3.脂肪的氧化需要消耗大量的氧气,而糖类在有氧无氧的情况下都能氧化、
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/biopy/p/4732992.html