标签:
1、[NSBundle mainBundle],文件夹其实是Group,如左侧的树形文件管理器
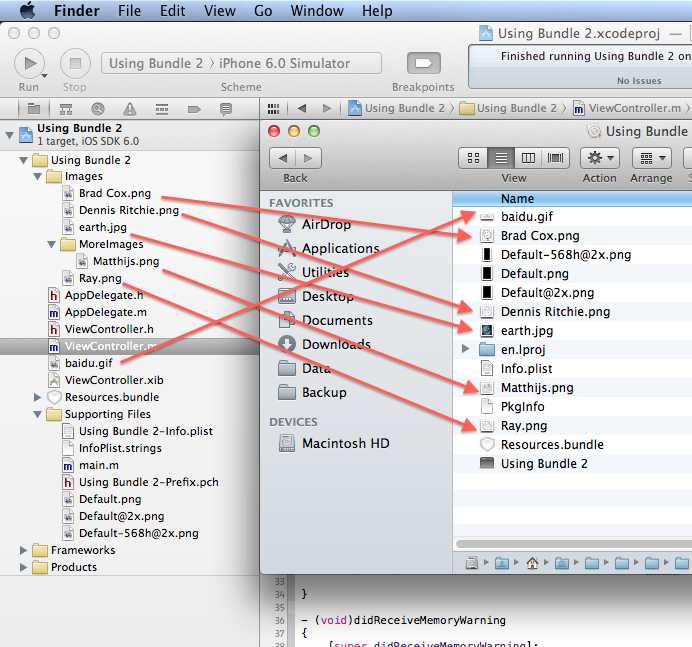
Build之后,文件直接就复制到了根目录下,于是读取的方法,应该是这样:
NSString *earth = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"Brad Cox" ofType:@"png"]; |
2、使用文件夹的时候,Build结果
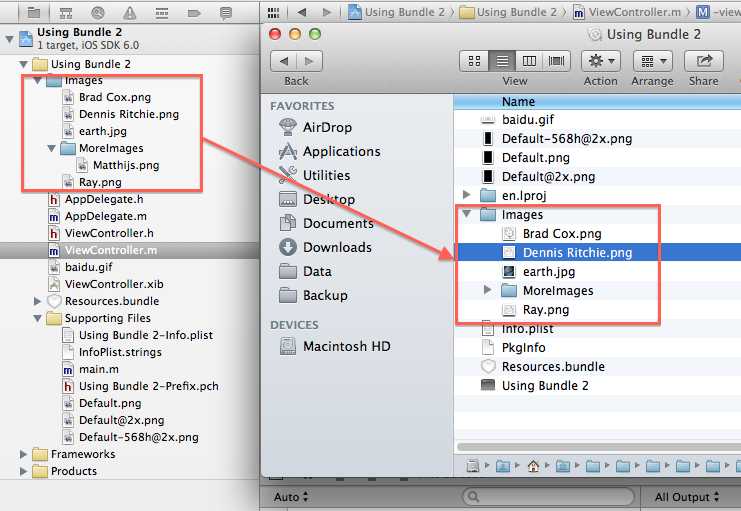
依然使用同样的方法,不需要制定文件夹路径
//inDirectory参数可有可无
NSString *earth = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"Matthijs" ofType:@"png" inDirectory:@"Images/MoreImages"]; NSString *earth = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"Matthijs" ofType:@"png"];
编译之后,mainBundle的资源都是放到RootFolder下,所以,可以直接访问,不要指定内部路径
3、使用其他的Bundle
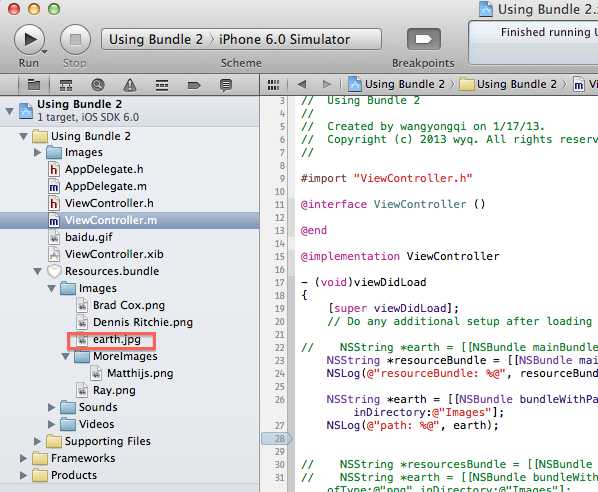
NSString *resourceBundle = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"Resources" ofType:@"bundle"]; NSLog(@"resourceBundle: %@", resourceBundle); NSString *earth = [[NSBundlebundleWithPath:resourceBundle] pathForResource:@"Matthijs"ofType:@"jpg"inDirectory:@"Images/MoreImages"]; NSLog(@"path: %@", earth); |
使用Custom bundle,访问内部的子文件夹,需要指定inDirectory参数,这个mainBundle不同,这是为何?
注意:Sincebundles other than the main bundle can have folders embedded inside them, to accessfiles inside folders of a bundle other than the main bundle it is best to use the pathForResource:ofType:inDirectory: method of NSBundle to explicitly specify the folder inwhich a specific file/resource exists. |
NSBundle的使用,注意mainBundle和Custom Bundle的区别
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kenshinobiy/p/4735923.html