标签:
电脑配置:
操作系统:window 8.1
Matlab 2012a安装路径:D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a
VS2010 :
OpenCV 2.4.3:D:\Program Files\opencv
补充说明:
在配置前,先检查一下系统变量:
1.若缺少系统变量(该路径必须添加!!!):
D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a\runtime\win64
导致结果:程序无法正常启动0x000007b。请单击“确定”关闭应用程序
注意变量配置后记得重启才会生效,而且添加路径要在英文符号下加入” ; ”,末尾不需要加分号!!!!
2.其他变量:可加可不加,经验证不会影响结果!!!
(1)用户变量:
D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a\bin\win64
D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a\runtime\win64
(2)系统变量:
D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a\bin\win64
本文转自博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/newpanderking/articles/4057977.html
1、背景
众所周知,matlab在处理矩阵、数学计算、计算机仿真、图像处理等方面有着 c c++无可比拟的优势,但是做成系统供使用时,又显得过于粗糙,为了使用起来高大上,计算起来有简单,方便。无疑,c++ 与matlab混合编程将会使非常靠谱的选择。
这里暂且不论所谓的matlab效率低,c/c++效率高的问题,自我感觉,以我目前编码的功底,所编写的代码的效率远远不及matlab提供的代码的效率。除非你是大牛,或者你是人云亦云,所以能用matlab混合c++编码还是很不错的选择,话不多说,我们开始讨论正题。
2、我使用的版本是matlab2012与vs2010混合编程的。
软件的下载这里就不多说了,我相信看这篇教程的你,这两个软件已经安装的妥妥当当的了。
这里我选用网上常用来做例子的matlab代码做测试,spline.m,该文件位于
D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a\toolbox\matlab\polyfun
当然该文件中依赖调用另一个文件chckxy.m,该文件也在这条路径下。找到后复制到matlab的工作目录下。
这里为了方便提供两个文件的代码:
spline.m
1 function output = spline(x,y,xx) 2 %SPLINE Cubic spline data interpolation. 3 % PP = SPLINE(X,Y) provides the piecewise polynomial form of the 4 % cubic spline interpolant to the data values Y at the data sites X, 5 % for use with the evaluator PPVAL and the spline utility UNMKPP. 6 % X must be a vector. 7 % If Y is a vector, then Y(j) is taken as the value to be matched at X(j), 8 % hence Y must be of the same length as X -- see below for an exception 9 % to this. 10 % If Y is a matrix or ND array, then Y(:,...,:,j) is taken as the value to 11 % be matched at X(j), hence the last dimension of Y must equal length(X) -- 12 % see below for an exception to this. 13 % 14 % YY = SPLINE(X,Y,XX) is the same as YY = PPVAL(SPLINE(X,Y),XX), thus 15 % providing, in YY, the values of the interpolant at XX. For information 16 % regarding the size of YY see PPVAL. 17 % 18 % Ordinarily, the not-a-knot end conditions are used. However, if Y contains 19 % two more values than X has entries, then the first and last value in Y are 20 % used as the endslopes for the cubic spline. If Y is a vector, this 21 % means: 22 % f(X) = Y(2:end-1), Df(min(X))=Y(1), Df(max(X))=Y(end). 23 % If Y is a matrix or N-D array with SIZE(Y,N) equal to LENGTH(X)+2, then 24 % f(X(j)) matches the value Y(:,...,:,j+1) for j=1:LENGTH(X), then 25 % Df(min(X)) matches Y(:,:,...:,1) and Df(max(X)) matches Y(:,:,...:,end). 26 % 27 % Example: 28 % This generates a sine-like spline curve and samples it over a finer mesh: 29 % x = 0:10; y = sin(x); 30 % xx = 0:.25:10; 31 % yy = spline(x,y,xx); 32 % plot(x,y,‘o‘,xx,yy) 33 % 34 % Example: 35 % This illustrates the use of clamped or complete spline interpolation where 36 % end slopes are prescribed. In this example, zero slopes at the ends of an 37 % interpolant to the values of a certain distribution are enforced: 38 % x = -4:4; y = [0 .15 1.12 2.36 2.36 1.46 .49 .06 0]; 39 % cs = spline(x,[0 y 0]); 40 % xx = linspace(-4,4,101); 41 % plot(x,y,‘o‘,xx,ppval(cs,xx),‘-‘); 42 % 43 % Class support for inputs x, y, xx: 44 % float: double, single 45 % 46 % See also INTERP1, PCHIP, PPVAL, MKPP, UNMKPP. 47 48 % Carl de Boor 7-2-86 49 % Copyright 1984-2010 The MathWorks, Inc. 50 % $Revision: 5.18.4.6 $ $Date: 2010/09/02 13:36:29 $ 51 52 53 % Check that data are acceptable and, if not, try to adjust them appropriately 54 [x,y,sizey,endslopes] = mychckxy(x,y); 55 n = length(x); yd = prod(sizey); 56 57 % Generate the cubic spline interpolant in ppform 58 59 dd = ones(yd,1); dx = diff(x); divdif = diff(y,[],2)./dx(dd,:); 60 if n==2 61 if isempty(endslopes) % the interpolant is a straight line 62 pp=mkpp(x,[divdif y(:,1)],sizey); 63 else % the interpolant is the cubic Hermite polynomial 64 pp = pwch(x,y,endslopes,dx,divdif); pp.dim = sizey; 65 end 66 elseif n==3&&isempty(endslopes) % the interpolant is a parabola 67 y(:,2:3)=divdif; 68 y(:,3)=diff(divdif‘)‘/(x(3)-x(1)); 69 y(:,2)=y(:,2)-y(:,3)*dx(1); 70 pp = mkpp(x([1,3]),y(:,[3 2 1]),sizey); 71 else % set up the sparse, tridiagonal, linear system b = ?*c for the slopes 72 b=zeros(yd,n); 73 b(:,2:n-1)=3*(dx(dd,2:n-1).*divdif(:,1:n-2)+dx(dd,1:n-2).*divdif(:,2:n-1)); 74 if isempty(endslopes) 75 x31=x(3)-x(1);xn=x(n)-x(n-2); 76 b(:,1)=((dx(1)+2*x31)*dx(2)*divdif(:,1)+dx(1)^2*divdif(:,2))/x31; 77 b(:,n)=... 78 (dx(n-1)^2*divdif(:,n-2)+(2*xn+dx(n-1))*dx(n-2)*divdif(:,n-1))/xn; 79 else 80 x31 = 0; xn = 0; b(:,[1 n]) = dx(dd,[2 n-2]).*endslopes; 81 end 82 dxt = dx(:); 83 c = spdiags([ [x31;dxt(1:n-2);0] ... 84 [dxt(2);2*(dxt(2:n-1)+dxt(1:n-2));dxt(n-2)] ... 85 [0;dxt(2:n-1);xn] ],[-1 0 1],n,n); 86 87 % sparse linear equation solution for the slopes 88 mmdflag = spparms(‘autommd‘); 89 spparms(‘autommd‘,0); 90 s=b/c; 91 spparms(‘autommd‘,mmdflag); 92 93 % construct piecewise cubic Hermite interpolant 94 % to values and computed slopes 95 pp = pwch(x,y,s,dx,divdif); pp.dim = sizey; 96 97 end 98 99 if nargin==2, output = pp; else output = ppval(pp,xx); end
chckxy.m
1 function [x,y,sizey,endslopes] = mychckxy(x,y) 2 %CHCKXY check and adjust input for SPLINE and PCHIP 3 % [X,Y,SIZEY] = CHCKXY(X,Y) checks the data sites X and corresponding data 4 % values Y, making certain that there are exactly as many sites as values, 5 % that no two data sites are the same, removing any data points that involve 6 % NaNs, reordering the sites if necessary to ensure that X is a strictly 7 % increasing row vector and reordering the data values correspondingly, 8 % and reshaping Y if necessary to make sure that it is a matrix, with Y(:,j) 9 % the data value corresponding to the data site X(j), and with SIZEY the 10 % actual dimensions of the given values. 11 % This call to CHCKXY is suitable for PCHIP. 12 % 13 % [X,Y,SIZEY,ENDSLOPES] = CHCKXY(X,Y) also considers the possibility that 14 % there are two more data values than there are data sites. 15 % If there are, then the first and the last data value are removed from Y 16 % and returned separately as ENDSLOPES. Otherwise, an empty ENDSLOPES is 17 % returned. This call to CHCKXY is suitable for SPLINE. 18 % 19 % See also PCHIP, SPLINE. 20 21 % Copyright 1984-2011 The MathWorks, Inc. 22 23 % make sure X is a vector: 24 if length(find(size(x)>1))>1 25 error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:XNotVector‘)) 26 end 27 28 % ensure X is real 29 if any(~isreal(x)) 30 error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:XComplex‘)) 31 end 32 33 % deal with NaN‘s among the sites: 34 nanx = find(isnan(x)); 35 if ~isempty(nanx) 36 x(nanx) = []; 37 warning(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:nan‘)) 38 end 39 40 n=length(x); 41 if n<2 42 error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:NotEnoughPts‘)) 43 end 44 45 % re-sort, if needed, to ensure strictly increasing site sequence: 46 x=x(:).‘; 47 dx = diff(x); 48 49 if any(dx<0), [x,ind] = sort(x); dx = diff(x); else ind=1:n; end 50 51 if ~all(dx), error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:RepeatedSites‘)), end 52 53 % if Y is ND, reshape it to a matrix by combining all dimensions but the last: 54 sizey = size(y); 55 56 57 while length(sizey)>2&&sizey(end)==1, sizey(end) = []; end 58 59 60 yn = sizey(end); 61 sizey(end)=[]; 62 yd = prod(sizey); 63 64 if length(sizey)>1 65 y = reshape(y,yd,yn); 66 else 67 % if Y happens to be a column matrix, change it to the expected row matrix. 68 if yn==1 69 yn = yd; 70 y = reshape(y,1,yn); 71 yd = 1; 72 sizey = yd; 73 end 74 end 75 76 % determine whether not-a-knot or clamped end conditions are to be used: 77 nstart = n+length(nanx); 78 if yn==nstart 79 endslopes = []; 80 elseif nargout==4&&yn==nstart+2 81 endslopes = y(:,[1 n+2]); y(:,[1 n+2])=[]; 82 if any(isnan(endslopes)) 83 error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:EndslopeNaN‘)) 84 end 85 if any(isinf(endslopes)) 86 error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:EndslopeInf‘)) 87 end 88 else 89 error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:NumSitesMismatchValues‘,nstart, yn)) 90 end 91 92 % deal with NaN‘s among the values: 93 if ~isempty(nanx) 94 y(:,nanx) = []; 95 end 96 97 y=y(:,ind); 98 nany = find(sum(isnan(y),1)); 99 if ~isempty(nany) 100 y(:,nany) = []; x(nany) = []; 101 warning(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:IgnoreNaN‘)) 102 n = length(x); 103 if n<2 104 error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:NotEnoughPts‘)) 105 end 106 end
function [x,y,sizey,endslopes] = mychckxy(x,y)
%CHCKXY check and adjust input for SPLINE and PCHIP
% [X,Y,SIZEY] = CHCKXY(X,Y) checks the data sites X and corresponding data
% values Y, making certain that there are exactly as many sites as values,
% that no two data sites are the same, removing any data points that involve
% NaNs, reordering the sites if necessary to ensure that X is a strictly
% increasing row vector and reordering the data values correspondingly,
% and reshaping Y if necessary to make sure that it is a matrix, with Y(:,j)
% the data value corresponding to the data site X(j), and with SIZEY the
% actual dimensions of the given values.
% This call to CHCKXY is suitable for PCHIP.
%
% [X,Y,SIZEY,ENDSLOPES] = CHCKXY(X,Y) also considers the possibility that
% there are two more data values than there are data sites.
% If there are, then the first and the last data value are removed from Y
% and returned separately as ENDSLOPES. Otherwise, an empty ENDSLOPES is
% returned. This call to CHCKXY is suitable for SPLINE.
%
% See also PCHIP, SPLINE.
% Copyright 1984-2011 The MathWorks, Inc.
% make sure X is a vector:
if length(find(size(x)>1))>1
error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:XNotVector‘))
end
% ensure X is real
if any(~isreal(x))
error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:XComplex‘))
end
% deal with NaN‘s among the sites:
nanx = find(isnan(x));
if ~isempty(nanx)
x(nanx) = [];
warning(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:nan‘))
end
n=length(x);
if n<2
error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:NotEnoughPts‘))
end
% re-sort, if needed, to ensure strictly increasing site sequence:
x=x(:).‘;
dx = diff(x);
if any(dx<0), [x,ind] = sort(x); dx = diff(x); else ind=1:n; end
if ~all(dx), error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:RepeatedSites‘)), end
% if Y is ND, reshape it to a matrix by combining all dimensions but the last:
sizey = size(y);
while length(sizey)>2&&sizey(end)==1, sizey(end) = []; end
yn = sizey(end);
sizey(end)=[];
yd = prod(sizey);
if length(sizey)>1
y = reshape(y,yd,yn);
else
% if Y happens to be a column matrix, change it to the expected row matrix.
if yn==1
yn = yd;
y = reshape(y,1,yn);
yd = 1;
sizey = yd;
end
end
% determine whether not-a-knot or clamped end conditions are to be used:
nstart = n+length(nanx);
if yn==nstart
endslopes = [];
elseif nargout==4&&yn==nstart+2
endslopes = y(:,[1 n+2]); y(:,[1 n+2])=[];
if any(isnan(endslopes))
error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:EndslopeNaN‘))
end
if any(isinf(endslopes))
error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:EndslopeInf‘))
end
else
error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:NumSitesMismatchValues‘,nstart, yn))
end
% deal with NaN‘s among the values:
if ~isempty(nanx)
y(:,nanx) = [];
end
y=y(:,ind);
nany = find(sum(isnan(y),1));
if ~isempty(nany)
y(:,nany) = []; x(nany) = [];
warning(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:IgnoreNaN‘))
n = length(x);
if n<2
error(message(‘MATLAB:chckxy:NotEnoughPts‘))
end
end
ps:说明下,由于这两个文件都是matlab的工具文件,所以chckxy.m在调用时,改了名字叫做mychckxy.m,相应的文件名字也需要改。
做一个简单的测试,做一个调用:
clc; clear all; close all; x = 0:10; y = sin(x); xx = 0:.25:10; yy = spline(x,y,xx) plot(x,y,‘o‘,xx,yy);
运行结果:
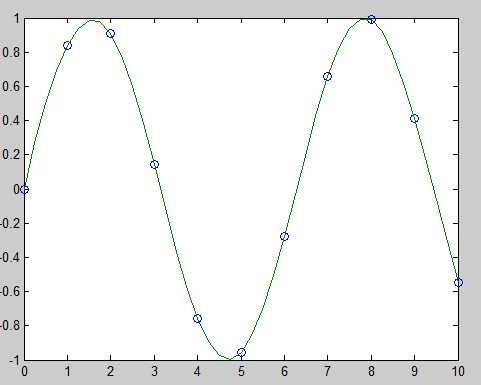

到此为止,都是准备工作做,下面开始介绍如何在vs中调用spline函数。
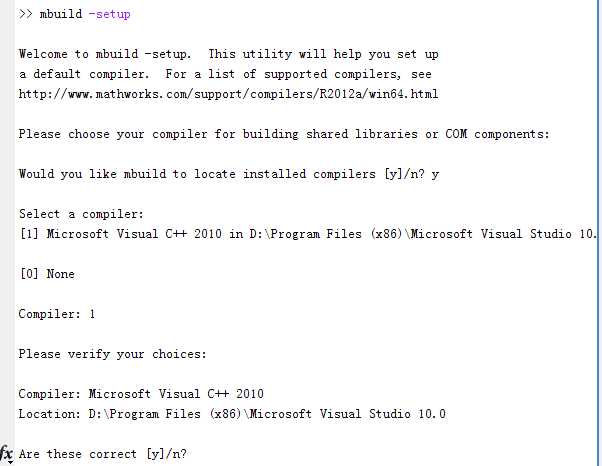
1)在matlab中输入命令 mbuild -setup , 运行结果如下图所示, 按照提示选择编译器 vs2010.
mbuild -setup
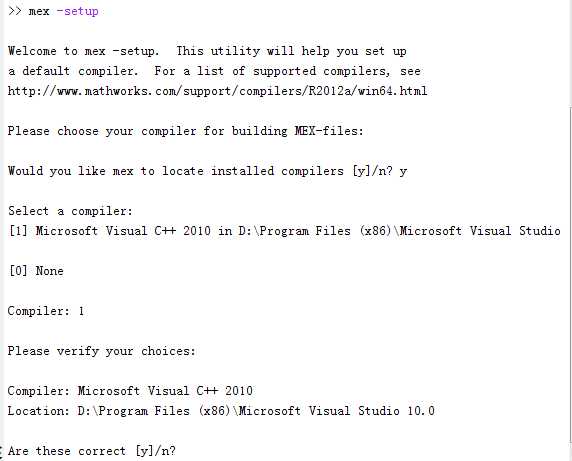
然后键入:mex -setup 命令,运行结果如下图所示,按照提示选择编译器 vs2010
mex -setup
然后在matlab命令窗口输入:
mcc -W cpplib:libspline -T link:lib spline.m
spline是名字,会根据.m文件的不同而不同!!!
或者输入:mcc -B csharedlib:name name.m
可以得到如下图这些文件:
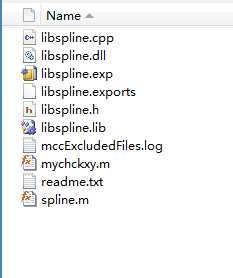
依然,其中的"libspline.dll"、"libspline.h"和"libspline.lib"这三个文件是我们所需的。
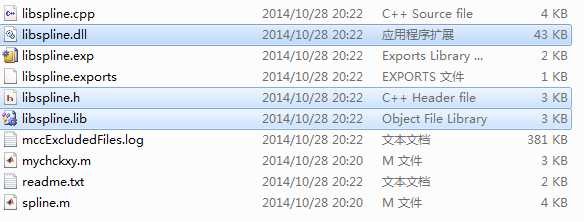
2)打开vs2010建一个控制台应用程序,可以选择一个空的控制台应用程序。
创建程序之后把第一步中得到的三个文件copy到工程中。
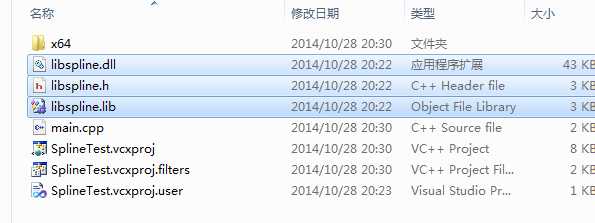
由于我的电脑是win 7 64bit(win8 64bit),matlab是64bit,所以应该选择x64,而不是win32平台。
a)修改平台参数,为x64
生成 ---> 配置管理器
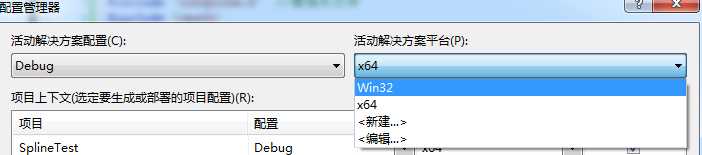
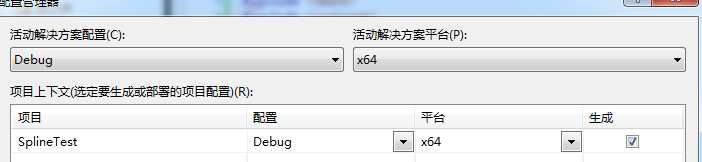
b)配置包含目录与库目录
项目 ----> 属性 ----> vc++目录
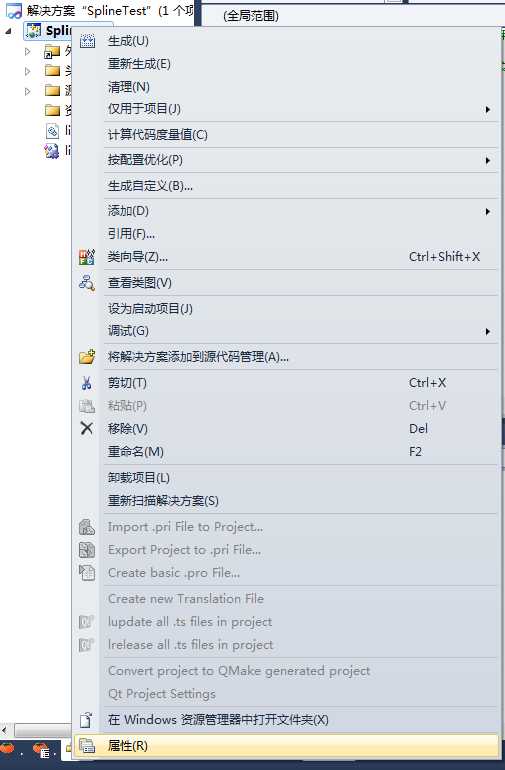
包含目录:
D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a\extern\include
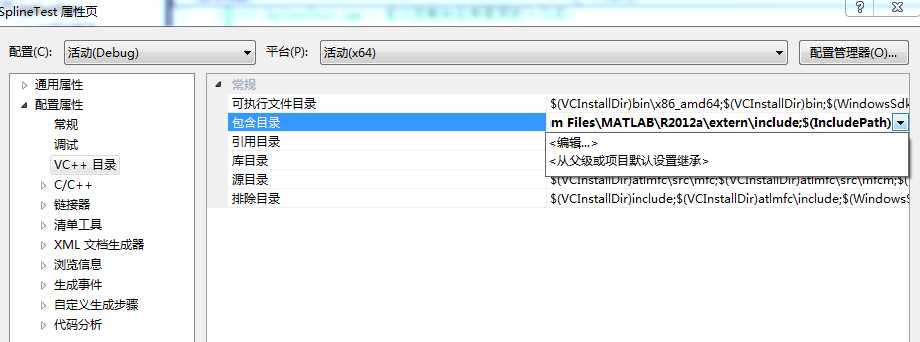
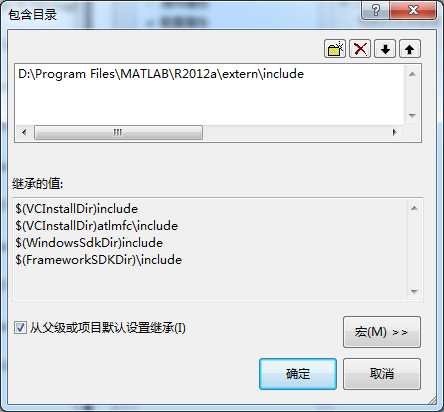
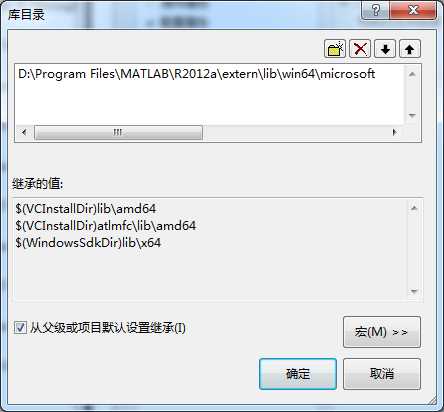
库目录:
D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a\extern\lib\win64\microsoft
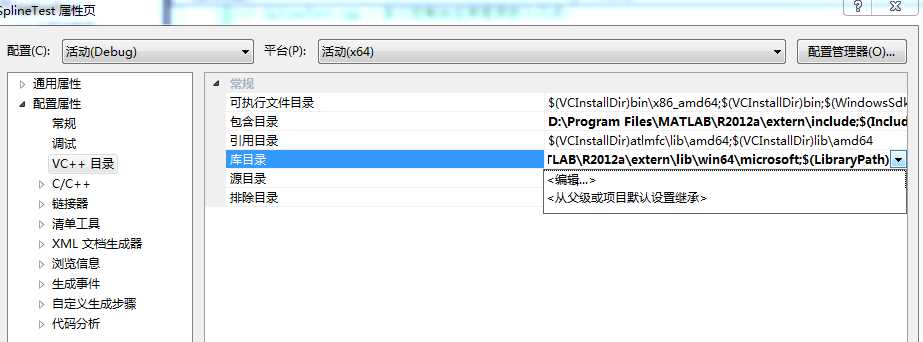
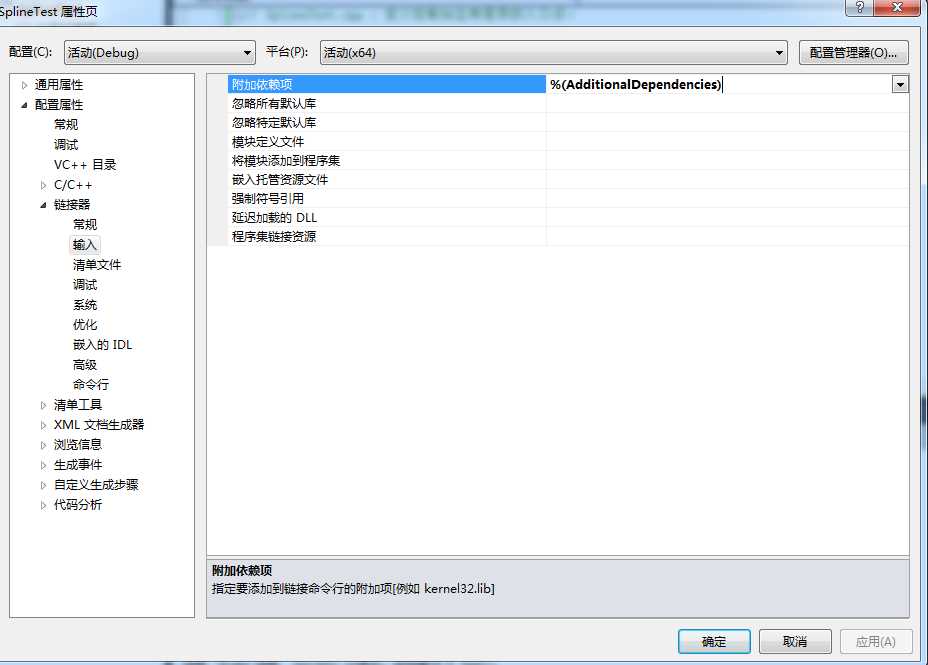
C1)配置附加依赖项
右键MatlabTest解决方案->属性->链接器->输入
在“附加依赖项中”中添加相应的静态链接库文件。对于需要添加的静态库文件的数量和名称,根据需要添加。
libmx.lib
libeng.lib
libmex.lib
libmat.lib
…………
根据需要后续补上。
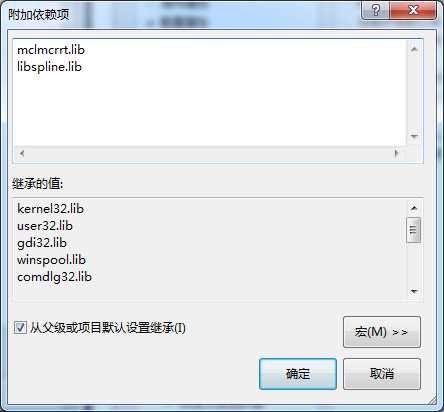
c2)配置附加依赖项 , 这里根据项目的不同,依赖的文件不同,这里测试依赖的是"mclmcrrt.lib"和"libspline.lib"这两个lib,第一是库lib,第二个是我们生成的lib.文件。所依赖的lib文件在库目录已经说明了,
路径为:D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2012a\extern\lib\win64\microsoft下。
这里有两种解决方案,第一种在vs中配置。
第一种在vs中配置。建议采用第二种方法!!!!因为第一种不同链接库配置的lib会不一样
项目 ----> 属性 ----> 连接器 ----> 输入
第二种方法是,在文件中直接引入lib文件。

做完以上工作后,我们新建一个主函数作为入口函数,具体测试代码如下:
#include "libspline.h" //增加头文件
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
#pragma comment(lib,"mclmcrrt.lib")
#pragma comment(lib,"libspline.lib")
int main()
{
//初始化lib(必须)
if (!libsplineInitialize())
return -1;
int i, j;
double x[1][11], y[1][11];
for(i=0; i<11; i++)
{
x[0][i] = i;
y[0][i] = sin(x[0][i]);
}
double xx[1][41];
for(i=0; i<41; i++)
xx[0][i] = i*0.25;
double yy[1][41];
mwArray mwX(1,11,mxDOUBLE_CLASS);
mwArray mwY(1,11,mxDOUBLE_CLASS);
mwArray mwXX(1,41,mxDOUBLE_CLASS);
mwArray mwYY(1,41,mxDOUBLE_CLASS);
mwX.SetData(*x, 11);
mwY.SetData(*y, 11);
mwXX.SetData(*xx, 41);
mwYY.SetData(*yy, 41);
spline(1, mwYY, mwX, mwY, mwXX); //调用spline
cout<<"yy = "<<endl;
i = 0;
for(j = 0; j < 41; j++)
{
//Get第一个参数表示用1个下标访问元素,j+1是列号(MATLAB下标从1开始,而C++从0开始,故做+1操作)
yy[0][j] = mwYY.Get(1,j+1);
cout<<setprecision(4)<<right<<setw(10)<<yy[0][j];
i++;
if(i%7 == 0) cout<<endl; //换行
}
cout<<endl;
//终止调用
libsplineTerminate();
return 0;
}
运行结果如图:
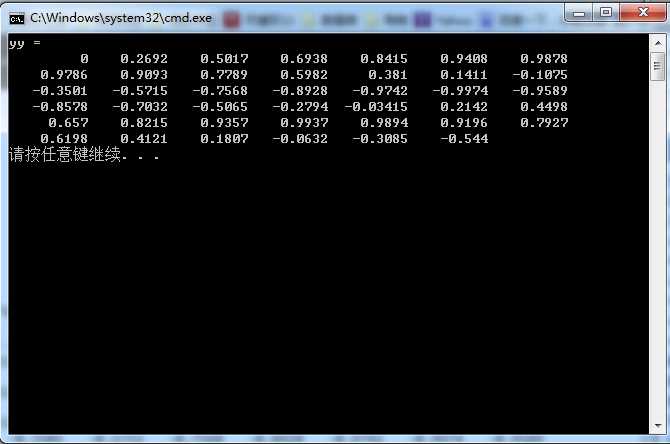
比较这个结果与最开始我们测试matlab运行的结果,测试通过。matlab配置完成。
ps说明:配置过程中遇到的问题:
配置时经常遇到 LINK2019的错误。这种错误就是典型的lib缺失导入的问题。
main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 mclGetMatrix_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: __cdecl mwArray::mwArray(unsigned __int64,unsigned __int64,enum mxClassID,enum mxComplexity)" (??0mwArray@@QEAA@_K0W4mxClassID@@W4mxComplexity@@@Z) 中被引用 1>main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 mclcppGetLastError_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: static void __cdecl mwException::raise_error(void)" (?raise_error@mwException@@SAXXZ) 中被引用 1>main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 mclcppCreateError_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: __cdecl mwException::mwException(void)" (??0mwException@@QEAA@XZ) 中被引用 1>main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 ref_count_obj_addref_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: __cdecl mwException::mwException(class mwException const &)" (??0mwException@@QEAA@AEBV0@@Z) 中被引用 1>main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 ref_count_obj_release_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: virtual __cdecl mwException::~mwException(void)" (??1mwException@@UEAA@XZ) 中被引用 1>main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 error_info_get_message_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: virtual char const * __cdecl mwException::what(void)const " (?what@mwException@@UEBAPEBDXZ) 中被引用 1>main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 array_ref_getV_int_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: class mwArray __cdecl mwArray::GetPromoted(unsigned __int64,...)" (?GetPromoted@mwArray@@QEAA?AV1@_KZZ) 中被引用 1>main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 array_ref_set_numeric_mxDouble_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: void __cdecl mwArray::SetData(double *,unsigned __int64)" (?SetData@mwArray@@QEAAXPEAN_K@Z) 中被引用 1>main.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 array_ref_get_numeric_mxDouble_proxy,该符号在函数 "public: __cdecl mwArray::operator double(void)const " (??BmwArray@@QEBANXZ) 中被引用
这里是因为缺少:mclmcrrt.lib
#pragma comment(lib,"mclmcrrt.lib")
即可解决。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/realkate1/p/4736072.html